Pd-Catalyzed Alkene Difunctionalization Reactions of Malonate Nucleophiles: Synthesis of Substituted Cyclopentanes via Alkene Aryl-Alkylation and Akenyl-Alkylation
- PMID: 31021646
- PMCID: PMC6996780
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01258
Pd-Catalyzed Alkene Difunctionalization Reactions of Malonate Nucleophiles: Synthesis of Substituted Cyclopentanes via Alkene Aryl-Alkylation and Akenyl-Alkylation
Abstract
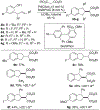
The Pd-catalyzed coupling of malonate nucleophiles with alkenes bearing tethered aryl or alkenyl triflates is described. These alkene difunctionalization reactions afford malonate-substituted cyclopentanes that contain fused aryl or cycloalkenyl rings. The transformations generate a five-membered ring, two C-C bonds, and provide products bearing up to three stereocenters with good chemical yield and generally high diastereoselectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Regiodivergent Palladium-Catalyzed Alkene Difunctionalization Reactions for the Construction of Methylene Cyclobutanes and Methylene Cyclopentanes.Org Lett. 2022 Nov 11;24(44):8208-8212. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03308. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Org Lett. 2022. PMID: 36315977 Free PMC article.
-
Pd-Catalyzed Alkene Difunctionalization Reactions of Enolates for the Synthesis of Substituted Bicyclic Cyclopentanes.Org Process Res Dev. 2019 Aug 16;23(8):1610-1630. doi: 10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00248. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Org Process Res Dev. 2019. PMID: 33597795 Free PMC article.
-
Stereocontrolled synthesis of bicyclic sulfamides via Pd-catalyzed alkene carboamination reactions. Control of 1,3-asymmetric induction by manipulating mechanistic pathways.Org Lett. 2014 Jun 20;16(12):3412-5. doi: 10.1021/ol5015976. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Org Lett. 2014. PMID: 24916343 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrogenative Pd and Ni Catalysis for Total Synthesis.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Mar 2;54(5):1118-1130. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00787. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33592147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enantioselective Dicarbofunctionalization of Unactivated Alkenes by Palladium-Catalyzed Tandem Heck/Suzuki Coupling Reaction.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Oct 7;58(41):14653-14659. doi: 10.1002/anie.201907840. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31420928 Review.
Cited by
-
Ni-Catalyzed Arylbenzylation of Alkenylarenes: Kinetic Studies Reveal Autocatalysis by ZnX2 *.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Oct 11;60(42):22977-22982. doi: 10.1002/anie.202110459. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 34427992 Free PMC article.
-
Regiodivergent Palladium-Catalyzed Alkene Difunctionalization Reactions for the Construction of Methylene Cyclobutanes and Methylene Cyclopentanes.Org Lett. 2022 Nov 11;24(44):8208-8212. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03308. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Org Lett. 2022. PMID: 36315977 Free PMC article.
-
Transition Metal (Ni, Cu, Pd)-Catalyzed Alkene Dicarbofunctionalization Reactions.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Sep 7;54(17):3415-3437. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00329. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34383469 Free PMC article.
-
Pd-Catalyzed C-C, C-N, and C-O Bond-Forming Difunctionalization Reactions of Alkenes Bearing Tethered Aryl/Alkenyl Triflates.Isr J Chem. 2020 Mar;60(3-4):259-267. doi: 10.1002/ijch.201900108. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Isr J Chem. 2020. PMID: 33664525 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 2-Cyanomethyl Indane Derivatives via Pd-Catalyzed Alkene Difunctionalization Reactions of Alkyl Nitriles.Org Lett. 2023 Apr 28;25(16):2767-2770. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00571. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Org Lett. 2023. PMID: 37071777 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
For a review, see:
- Dhungana RK; KC S; Basnet P; Giri R Chem. Rec 2018, 18, 1314. - PubMed
-
For selected recent examples, see
- KC S; Basnet P; Thapa S; Shrestha B; Giri R J. Org. Chem 2018, 83, 2920. - PubMed
- Kuang Y; Wang X; Anthony D; Diao T Chem. Commun 2018, 54, 2558. - PubMed
- Wang K; Ding Z; Zhou Z; Kong W J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 12364. - PubMed
- Basnet P; Dhungana RK; Thapa S; Shrestha B; KC S; Sears JM; Giri R J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 7782. - PubMed
- Derosa J; Tran VT; Boulous MN; Chen JS; Engle KM J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 10657. - PubMed
- Derosa J; van der Puyl VA; Tran VT; Liu M; Engle KM Chem. Sci 2018, 9, 5278. - PMC - PubMed
- Liu Z; Zeng T; Yang KS; Engle KM J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 15122. - PubMed
- Kirsch JK; Manske JL; Wolfe JP J. Org. Chem 2018, 83, 13568. - PMC - PubMed
-
-
- White DR; Herman MI; Wolfe JP Org. Lett 2017, 19, 4311. - PubMed
-
- Iwata C; Kubota H; Yamada M; Takemoto Y; Uchida S; Tanaka T; Imanishi T Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 3339.
- Iwata C; Takemoto Y; Kubota H Kuroda T; Imanishi T Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 3231.
- Muraoka M; Toshio N; Sugie A; Ono K; Yamamoto M US Patent 4,680,307, 1987.
-
-
Related 2-cyclopentylacetic acid derivatives that would derive from saponification and decarboxylation of the products have also found utility as synthetic intermediates. For representative examples, see:
- Taber DF; Paquette CM; J. Org. Chem 2014, 79, 3410. - PubMed
- Srikrishna A; Beerahah B Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 2291.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

