ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Filoviridae
- PMID: 31021739
- PMCID: PMC7011696
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001252
ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Filoviridae
Abstract
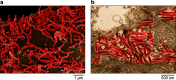
Members of the family Filoviridae produce variously shaped, often filamentous, enveloped virions containing linear non-segmented, negative-sense RNA genomes of 15-19 kb. Several filoviruses (e.g., Ebola virus) are pathogenic for humans and are highly virulent. Several filoviruses infect bats (e.g., Marburg virus), whereas the hosts of most other filoviruses are unknown. This is a summary of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Report on Filoviridae, which is available at www.ictv.global/report/filoviridae.
Keywords: Filoviridae; ICTV Report; ebolavirus; filovirus; marburgvirus; taxonomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brauburger K, Deflubé LR, Mühlberger E. Filovirus transcription and replication. In: Pattnaik AK, Whitt MA, editors. Biology and Pathogenesis of Rhabdo- and Filoviruses. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing; 2015. pp. 515–555. (editors)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

