HMGB proteins are required for sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 31022275
- PMCID: PMC6483251
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216094
HMGB proteins are required for sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
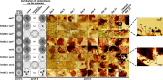
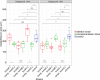
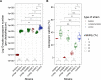
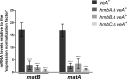
Aspergillus nidulans has three high mobility group box (HMGB) proteins, HmbA, HmbB and HmbC that are chromatin-associated architectural proteins involved in DNA-related functions. By creating and studying deletion strains in both veA+ and veA1 background, we have characterized the role of HmbA, HmbB and HmbC in sexual development. Expression of the mating-type MAT1-1 and MAT1-2 coding genes were found to be extremely down-regulated in all three mutants on day 4 of sexual development, which results in deficient ascospore production and/or ascospore viability in the mutants. In addition, we found that HmbA and HmbB play also a role in sensing of and response to environmental signals, while HmbC functionally interacts with VeA, a key regulator of the coordination of asexual and sexual development, as well as of secondary metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the Aspergillus nidulans high mobility group B protein HmbA, the orthologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Nhp6p.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 15;12(1):17334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22202-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36243791 Free PMC article.
-
A dually located multi-HMG-box protein of Aspergillus nidulans has a crucial role in conidial and ascospore germination.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Oct;94(2):383-402. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12772. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25156107
-
The asexual pathogen aspergillus fumigatus expresses functional determinants of Aspergillus nidulans sexual development.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Oct;7(10):1724-32. doi: 10.1128/EC.00157-08. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18757566 Free PMC article.
-
The VeA regulatory system and its role in morphological and chemical development in fungi.Fungal Genet Biol. 2008 Jul;45(7):1053-61. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Fungal Genet Biol. 2008. PMID: 18457967 Review.
-
Spotlight on Aspergillus nidulans photosensory systems.Fungal Genet Biol. 2010 Nov;47(11):900-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2010.05.008. Epub 2010 May 23. Fungal Genet Biol. 2010. PMID: 20573560 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Chromatin and Transcriptional Control in the Formation of Sexual Fruiting Bodies in Fungi.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2022 Dec 21;86(4):e0010422. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00104-22. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36409109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Peroxisomes and Mitochondria during Fungal Development.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Nov 20;6(4):302. doi: 10.3390/jof6040302. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33233491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HmbC, a Protein of the HMG Family, Participates in the Regulation of Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Fusarium fujikuroi.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 21;14(8):1661. doi: 10.3390/genes14081661. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628712 Free PMC article.
-
The Pheromone Module SteC-MkkB-MpkB-SteD-HamE Regulates Development, Stress Responses and Secondary Metabolism in Aspergillus fumigatus.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 7;11:811. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00811. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32457716 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the Aspergillus nidulans high mobility group B protein HmbA, the orthologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Nhp6p.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 15;12(1):17334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22202-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36243791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bustin M. Revised nomenclature for high mobility group (HMG) chromosomal proteins. Trends in biochemical sciences. 2001;26(3):152–3. Epub 2001/03/14. S0968-0004(00)01777-1 [pii]. . - PubMed
-
- Bustin M, Reeves R. High-mobility-group chromosomal proteins: architectural components that facilitate chromatin function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1996;54:35–100. Epub 1996/01/01. . - PubMed
-
- Thomas JO, Travers AA. HMG1 and 2, and related 'architectural' DNA-binding proteins. Trends in biochemical sciences. 2001;26(3):167–74. Epub 2001/03/14. S0968-0004(01)01801-1 [pii]. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

