Feasibility of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging for Rapid Detection of Thiophanate-Methyl Residue on Mulberry Fruit
- PMID: 31022906
- PMCID: PMC6515382
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20082017
Feasibility of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging for Rapid Detection of Thiophanate-Methyl Residue on Mulberry Fruit
Abstract
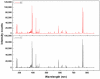
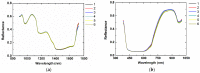
An effective and rapid way to detect thiophanate-methyl residue on mulberry fruit is important for providing consumers with quality and safe of mulberry fruit. Chemical methods are complex, time-consuming, and costly, and can result in sample contamination. Rapid detection of thiophanate-methyl residue on mulberry fruit was studied using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and hyperspectral imaging (HSI) techniques. Principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least square regression (PLSR) were used to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the data obtained by using LIBS and HSI on mulberry fruit samples with different thiophanate-methyl residues. The competitive adaptive reweighted sampling algorithm was used to select optimal variables. The results of model calibration were compared. The best result was given by the PLSR model that used the optimal preprocessed LIBS-HSI variables, with a correlation coefficient of 0.921 for the prediction set. The results of this research confirmed the feasibility of using LIBS and HSI for the rapid detection of thiophanate-methyl residue on mulberry fruit.
Keywords: chemometrics; hyperspectral imaging; laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy; mulberry; pesticide residue; variable selection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kim A.-J., Kim M.-W., Woo N.-R.-Y., Kim S.-Y., Kim H.-B., Lim Y.-H., Kim M.-H. Study on the nutritional composition and antioxidative capacity of mulberry fruit (Ficus-4x) Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004;36:995–1000.
-
- Li Y.-F., Qiao L.-Q., Li F.-W., Ding Y., Yang Z.-J., Wang M.-L. Determination of multiple pesticides in fruits and vegetables using a modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe method with magnetic nanoparticles and gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2014;1361:77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tong H., Tong Y., Xue J., Liu D., Wu X. Multi-residual pesticide monitoring in commercial Chinese herbal medicines by gas chromatography–triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Meth. 2014;7:135–145. doi: 10.1007/s12161-013-9609-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

