ER and Nutrient Stress Promote Assembly of Respiratory Chain Supercomplexes through the PERK-eIF2α Axis
- PMID: 31023583
- PMCID: PMC6555668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.031
ER and Nutrient Stress Promote Assembly of Respiratory Chain Supercomplexes through the PERK-eIF2α Axis
Abstract
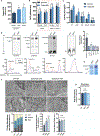
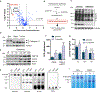
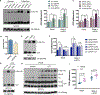
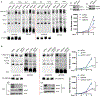
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and unfolded protein response are energetically challenging under nutrient stress conditions. However, the regulatory mechanisms that control the energetic demand under nutrient and ER stress are largely unknown. Here we show that ER stress and glucose deprivation stimulate mitochondrial bioenergetics and formation of respiratory supercomplexes (SCs) through protein kinase R-like ER kinase (PERK). Genetic ablation or pharmacological inhibition of PERK suppresses nutrient and ER stress-mediated increases in SC levels and reduces oxidative phosphorylation-dependent ATP production. Conversely, PERK activation augments respiratory SCs. The PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 axis increases supercomplex assembly factor 1 (SCAF1 or COX7A2L), promoting SCs and enhanced mitochondrial respiration. PERK activation is sufficient to rescue bioenergetic defects caused by complex I missense mutations derived from mitochondrial disease patients. These studies have identified an energetic communication between ER and mitochondria, with implications in cell survival and diseases associated with mitochondrial failures.
Keywords: ATF4; ER stress; PERK; hexosamine pathway; mitochondria; mitochondrial cristae; mitochondrial diseases; nutrient stress; protein glycosylation; respiratory chain supercomplexes.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
ER stress boosts respiration.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Aug;20(8):453. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0139-x. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31053825 No abstract available.
-
ER Stress Priming of Mitochondrial Respiratory suPERKomplex Assembly.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Oct;30(10):685-687. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.08.003. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31455568
References
-
- Acin-Perez R, Fernandez-Silva P, Peleato ML, Perez-Martos A, and Enriquez JA (2008). Respiratory active mitochondrial supercomplexes. Mol Cell 32, 529–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

