Boron Doped Diamond Electrodes in Flow-Based Systems
- PMID: 31024886
- PMCID: PMC6463006
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00190
Boron Doped Diamond Electrodes in Flow-Based Systems
Abstract
Boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes present several notable properties, such as the largest potential window of all electrode materials (especially in anodic potentials), low background and capacitive currents, reduced fouling compared to other electrodes, mechanical robustness, and good stability over time. On the other hand, flow-based systems are known as well-established approaches to minimize reagent consumption and waste generation and with good compromise between sample throughput and analytical performance (mechanization of chemical assays). This review focuses on the use of BDD electrodes for electrochemical detection in flow systems, such as flow injection analysis (FIA), batch injection analysis (BIA), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and capillary electrophoresis (CE). The discussion deals with the historical evolution of BDD, types of electrochemical pre-treatments (cathodically/H-terminated or anodically/O-terminated), cell configurations, and analytical performance. Articles are discussed in chronological order and subdivided according to the type of flow system: FIA, BIA, HPLC, and CE.
Keywords: batch injection analysis; capillary electrophoresis; flow injection analysis; liquid chromatography; review.
Figures
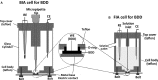
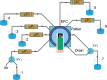
References
-
- Ṙužič J., Hansen E. H. (1975). Flow injection analyses. Anal. Chim. Acta. 78, 145–157. 10.1016/S0003-2670(01)84761-9 - DOI
-
- Alecrim M. F., Oliveira F. M., Guedes T. J., Neves C. D. C., Mendonça V. A., Gil E. S., et al. (2016). Electrochemical behavior of the cotinine at a boron-doped diamond electrode and its determination in saliva by multiple-pulse amperometry in an FIA system. Electrochim. Acta. 222, 331–337. 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.10.177 - DOI
-
- Alencar L. M., de Oliveira L. H., Backes R., Rosa T. M., de Oliveira P. R., da Silva R. A. B., et al. (2017). Liquid-liquid extraction coupled to batch injection analysis for electroanalysis of levofloxacin at low concentration level. Electroanalysis. 29, 2559–2564. 10.1002/elan.201700364 - DOI
-
- Andrade L. S., de Moraes M. C., Rocha-Filho R. C., Fatibello-Filho O., Cass Q. B. (2009). A multidimensional high performance liquid chromatography method coupled with amperometric detection using a boron-doped diamond electrode for the simultaneous determination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in bovine milk. Anal. Chim. Acta. 654, 127–132. 10.1016/j.aca.2009.09.035 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

