Interventions for hand eczema
- PMID: 31025714
- PMCID: PMC6484375
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004055.pub2
Interventions for hand eczema
Abstract
Background: Hand eczema is an inflammation of the skin of the hands that tends to run a chronic, relapsing course. This common condition is often associated with itch, social stigma, and impairment in employment. Many different interventions of unknown effectiveness are used to treat hand eczema.
Objectives: To assess the effects of topical and systemic interventions for hand eczema in adults and children.
Search methods: We searched the following up to April 2018: Cochrane Skin Group Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, AMED, LILACS, GREAT, and four trials registries. We checked the reference lists of included studies for further references to relevant trials.
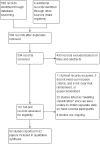
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that compared interventions for hand eczema, regardless of hand eczema type and other affected sites, versus no treatment, placebo, vehicle, or active treatments.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane. Primary outcomes were participant- and investigator-rated good/excellent control of symptoms, and adverse events.
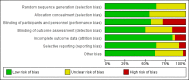
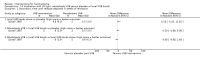
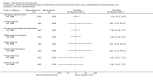
Main results: We included 60 RCTs, conducted in secondary care (5469 participants with mild to severe chronic hand eczema). Most participants were over 18 years old. The duration of treatment was short, generally up to four months. Only 24 studies included a follow-up period. Clinical heterogeneity in treatments and outcome measures was evident. Few studies performed head-to-head comparisons of different interventions. Risk of bias varied considerably, with only five studies at low risk in all domains. Twenty-two studies were industry-funded.Eighteen trials studied topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors; 10 studies, phototherapy; three studies, systemic immunosuppressives; and five studies, oral retinoids. Most studies compared an active intervention against no treatment, variants of the same medication, or placebo (or vehicle). Below, we present results from the main comparisons.Corticosteroid creams/ointments: when assessed 15 days after the start of treatment, clobetasol propionate 0.05% foam probably improves participant-rated control of symptoms compared to vehicle (risk ratio (RR) 2.32, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.38 to 3.91; number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 3, 95% CI 2 to 8; 1 study, 125 participants); the effect of clobetasol compared to vehicle for investigator-rated improvement is less clear (RR 1.43, 95% CI 0.86 to 2.40). More participants had at least one adverse event with clobetasol (11/62 versus 5/63; RR 2.24, 95% CI 0.82 to 6.06), including application site burning/pruritus. This evidence was rated as moderate certainty.When assessed 36 weeks after the start of treatment, mometasone furoate cream used thrice weekly may slightly improve investigator-rated symptom control compared to twice weekly (RR 1.23, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.61; 1 study, 72 participants) after remission is reached. Participant-rated symptoms were not measured. Some mild atrophy was reported in both groups (RR 1.76, 95% CI 0.45 to 6.83; 5/35 versus 3/37). This evidence was rated as low certainty.Irradiation with ultraviolet (UV) light: local combination ultraviolet light therapy (PUVA) may lead to improvement in investigator-rated symptom control when compared to local narrow-band UVB after 12 weeks of treatment (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.22 to 1.16; 1 study, 60 participants). However, the 95% CI indicates that PUVA might make little or no difference. Participant-rated symptoms were not measured. Adverse events (mainly erythema) were reported by 9/30 participants in the narrow-band UVB group versus none in the PUVA group. This evidence was rated as moderate certainty.Topical calcineurin inhibitors: tacrolimus 0.1% over two weeks probably improves investigator-rated symptom control measured after three weeks compared to vehicle (14/14 tacrolimus versus 0/14 vehicle; 1 study). Participant-rated symptoms were not measured. Four of 14 people in the tacrolimus group versus zero in the vehicle group had well-tolerated application site burning/itching.A within-participant study in 16 participants compared 0.1% tacrolimus to 0.1% mometasone furoate but did not measure investigator- or participant-rated symptoms. Both treatments were well tolerated when assessed at two weeks during four weeks of treatment.Evidence from these studies was rated as moderate certainty.Oral interventions: oral cyclosporin 3 mg/kg/d probably slightly improves investigator-rated (RR 1.88, 95% CI 0.88 to 3.99; 1 study, 34 participants) or participant-rated (RR 1.25, 95% CI 0.69 to 2.27) control of symptoms compared to topical betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% after six weeks of treatment. The risk of adverse events such as dizziness was similar between groups (up to 36 weeks; RR 1.22, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.86, n = 55; 15/27 betamethasone versus 19/28 cyclosporin). The evidence was rated as moderate certainty.Alitretinoin 10 mg improves investigator-rated symptom control compared with placebo (RR 1.58, 95% CI 1.20 to 2.07; NNTB 11, 95% CI 6.3 to 26.5; 2 studies, n = 781) and alitretinoin 30 mg also improves this outcome compared with placebo (RR 2.75, 95% CI 2.20 to 3.43; NNTB 4, 95% CI 3 to 5; 2 studies, n = 1210). Similar results were found for participant-rated symptom control: alitretinoin 10 mg RR 1.73 (95% CI 1.25 to 2.40) and 30 mg RR 2.75 (95% CI 2.18 to 3.48). Evidence was rated as high certainty. The number of adverse events (including headache) probably did not differ between alitretinoin 10 mg and placebo (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.55; 1 study, n = 158; moderate-certainty evidence), but the risk of headache increased with alitretinoin 30 mg (RR 3.43, 95% CI 2.45 to 4.81; 2 studies, n = 1210; high-certainty evidence). Outcomes were assessed between 48 and 72 weeks.
Authors' conclusions: Most findings were from single studies with low precision, so they should be interpreted with caution. Topical corticosteroids and UV phototherapy were two of the major standard treatments, but evidence is insufficient to support one specific treatment over another. The effect of topical calcineurin inhibitors is not certain. Alitretinoin is more effective than placebo in controlling symptoms, but advantages over other treatments need evaluating.Well-designed and well-reported, long-term (more than three months), head-to-head studies comparing different treatments are needed. Consensus is required regarding the definition of hand eczema and its subtypes, and a standard severity scale should be established.The main limitation was heterogeneity between studies. Small sample size impacted our ability to detect differences between treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
Wietske Andrea Christoffers: nothing to declare.
Pieter‐Jan Coenraads was involved in the included studies Ruzicka 2004, Ruzicka 2008, and van Coevorden 2004a.
Åke Svensson has been involved in educational events for Swedish dermatologists. Novartis has sponsored this event; however, the educational group have decided the content of the education, and no payment has been paid to Åke Svensson personally. Instead, payment has been made to his hospital for his time spent working outside hospital.
Thomas L Diepgen has received lecture and consultancy fees from Leo Pharma A/S and consultancy fees from Almirall Hermal GmbH, and he has co‐authored the studies of
Janine L Blok: nothing to declare.
Hywel Williams: nothing to declare.
Jun Xia: nothing to declare.
Figures



















































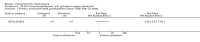



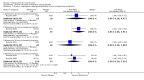



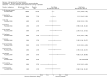




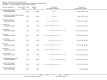







Comment in
-
Cochrane review "Interventions for hand eczema" is published.Contact Dermatitis. 2019 Sep;81(3):226. doi: 10.1111/cod.13324. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Contact Dermatitis. 2019. PMID: 31119748 No abstract available.
-
From the Cochrane Library: Interventions for hand eczema.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022 Feb;86(2):e31-e34. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.048. Epub 2021 Oct 1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34606772 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Adams 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Adams S, Bayerl C. Medium‐dose‐UVA‐1 irradiation ‐ and topical PUVA ‐ therapy in chronic dyshidrotic hand dermatitis ‐ a prospective randomized study [Mittel‐Dose‐UVA‐1‐ und lokale PUVA‐Therapie beim dyshidrosiformen Handekzem‐ eine prospektive randomisierte Studie]. Aktuelle Dermatologie 2007;33(4):142‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00642221; EMBASE: 2007235366]
Agarwal 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Agarwal US, Besarwal RK. Topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream alone and in combination with azathioprine in patients with chronic hand eczema: an observer blinded randomized comparative trial. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venerology, & Leprology 2013;79(1):101‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00877938; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Baskan 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Baskan EB, Kaçar SD, Tunali S. The efficacy of topical pimecrolimus cream 1% in hand dermatitis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2005;19(Suppl 2):267. [CENTRAL: CN‐00602438] - PubMed
-
- Baskan EB, Kaçar SD, Turan A, Tunali S. A new alternative in the treatment of hand eczema: topical pimecrolimus. Turkderm‐ Archieves of the Turkish Dermatology and Venerology 2007;41(4):125‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00708519]
Bauer 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bauer A, Lange N, Matterne U, Meurer M, Braeutigam M, Diepgen TL. Efficacy of pimecrolimus 1% cream in the long term management of atopic hand dermatitis. A double‐blind RCT. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft [Journal of the German Society of Dermatology] 2012;10(6):426‐33. [CENTRAL: CN‐00881946; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bayerl 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bayerl C, Garbea A, Peiler D, Rzany B, Allgäuer T, Kleesz P, et al. Pilot study for the treatment of occupational hand dermatitis with a new portable UVB irradiation unit [Pilotstudie zur Therapie des beruflich bedingten Handekzems mit einer neuen tragbaren UVB‐Bestrahlungseinheit]. Aktuelle Dermatologie 1999;25(10):302‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00414680; EMBASE: 1999385287]
Belsito 2004 {published data only}
-
- Belsito DV, Fowler JF Jr, Marks JG Jr, Pariser DM, Hanifin J, Duarte IA, et al. Pimecrolimus cream 1%: a potential new treatment for chronic hand dermatitis. Cutis 2004;73(1):31‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00471734; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bissonnette 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bissonnette R, Worm M, Gerlach B, Guenther L, Cambazard F, Ruzicka T, et al. Successful retreatment with alitretinoin in patients with relapsed chronic hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;162(2):420‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00751336; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bleeker 1989 {published data only}
-
- Bleeker J, Anagrius C, Iversen N, Stenberg B, Cullberg Valentin K. Double‐blind comparative study of Corticoderm® cream + unguentum Merck® and Betnovate® cream + unguentum Merck® in hand dermatitis. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1989;1(2):87‐90. [CENTRAL: CN‐00351307; EMBASE: 1990003851]
Boroujeni 2017 {published data only}
-
- Boroujeni HR, Parvin N, Mirzaeian P, Marandi S. Formulation and clinical trial study of AJMT cream in treatment of eczema. IIOAB Journal 2017;8:46‐50. [CENTRAL: CN‐01372398]
Brass 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Brass D, Farr P, Reynolds N, Stocken D, Macdonald C, Wahie S, et al. An observer‐blinded randomized controlled pilot study comparing localised psoralen‐ultraviolet A with localized narrowband ultraviolet B for the treatment of hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;173:13. [CENTRAL: CN‐01135916; EMBASE: 71969396] - PubMed
-
- ISRCTN18213910. Study comparing localised hand psoralen immersion combined with ultraviolet A (PUVA) with localised hand narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) for the treatment of hand eczema. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN18213910 (accessed 25 July 2017).
Burrows 1986 {published data only}
-
- Burrows D, Rogers S, Beck M, Kellet J, McMaster D, Merrett D, et al. Treatment of nickel dermatitis with Trientine. Contact Dermatitis 1986;15(2):55‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cartwright 1987 {published data only}
-
- Cartwright PH, Rowell NR. Comparison of Grenz rays versus placebo in the treatment of chronic hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 1987;117(1):73‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00050015; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cherill 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cherill R, Tofte S, MacNaul R, Maher T, Abrams B, Graeber M, et al. SDZ ASM 981 is effective in the treatment of chronic irritant hand dermatitis: a 6‐week randomized, double‐blind, vehicle‐controlled, single center study. Contact Dermatitis 2000;42 Suppl:16‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00400538]
Chu 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chu CY. A 4‐week randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, right‐left comparison study with E‐DO® in chronic hand dermatitis [Comparison study with E‐DO in chronic hand dermatitis]. Clinical Study Report 5 January 2009. [NCT00556855]
Faghihi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Faghihi G, Iraji F, Shahingohar A, Saidat A. The efficacy of '0.05% Clobetasol + 2.5% zinc sulphate' cream vs. '0.05% Clobetasol alone' cream in the treatment of the chronic hand eczema: a double‐blind study. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2008;22(5):531‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00630193; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fairris 1984 {published data only}
-
- Fairris GM, Mack DP, Rowell NR. Superficial X‐ray therapy in the treatment of constitutional eczema of the hands. British Journal of Dermatology 1984;111(4):445‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00568891; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fairris 1985 {published data only}
-
- Fairris GM, Jones DH, Mack DP, Rowell NR. Conventional superficial X‐ray versus Grenz ray therapy in the treatment of constitutional eczema of the hands. British Journal of Dermatology 1985;112(3):339‐41. [CENTRAL: CN‐00037293; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fowler 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fowler JF Jr, Fransway AF, Jackson JM, Rohowsky N. Hydrocortisone butyrate 0.1% cream in the treatment of chronic dermatitis. Cutis 2005;75(2):125‐31. [CENTRAL: CN‐00515029; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fowler 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fowler JF, Graff O, Hamedani AG. A phase 3, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study evaluating the efficacy and safety of alitretinoin (BAL4079) in the treatment of severe chronic hand eczema refractory to potent topical corticosteroid therapy. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2014;13(10):1198‐204. [CENTRAL: CN‐01110966] - PubMed
-
- NCT00817063. Efficacy and Safety of a Retinoid in the Treatment of Severe Chronic Hand Eczema (HANDEL). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00817063 (accessed 26 July 2017).
Fredriksson 1975 {published data only}
-
- Fredriksson T, Gip L. Urea creams in the treatment of dry skin and hand dermatitis. International Journal of Dermatology 1975;14(6):442‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00698353; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Granlund 1996 {published data only}
-
- Granlund H, Erkko P, Eriksson E, Reitamo S. Comparison of cyclosporine and topical betamethasone‐17,21‐dipropionate in the treatment of severe chronic hand eczema. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1996;76(5):371‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00132709; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Granlund H, Erkko P, Reitamo S. Comparison of the influence of cyclosporine and topical betamethasone‐17,21‐dipropionate treatment on quality of life in chronic hand eczema. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1997;77(1):54‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00137396; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Grattan 1991 {published data only}
-
- Grattan CE, Carmichael AJ, Shuttleworth GJ, Foulds IS. Comparison of topical PUVA with UVA for chronic vesicular hand eczema. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1991;71(2):118‐22. [CENTRAL: CN‐00075959; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gupta 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gupta AK, Shear NH, Lester RS, Baxter ML, Sauder DN. Betamethasone dipropionate polyacrylic film‐forming lotion in the treatment of hand dermatitis. International Journal of Dermatology 1993;32(11):828‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00097910; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hanifin 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hanifin JM, Stevens V, Sheth P, Breneman D. Novel treatment of chronic severe hand dermatitis with bexarotene gel. British Journal of Dermatology 2004;150(3):545‐53. [CENTRAL: CN‐00470992; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hill 1998 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Hill VA, Wong E, Corbett MF, Menday AP. Comparative efficacy of betamethasone/clioquinol (Betnovate‐C) cream and betamethasone/fusidic acid (Fucibet) cream in the treatment of infected hand eczema. Journal of Dermatological Treatment 1998;9(1):15‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00200945]
Hordinsky 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hordinsky M, Fleischer A, Rivers JK, Poulin Y, Belsito D, Hultsch T. Efficacy and safety of pimecrolimus cream 1% in mild‐to‐moderate chronic hand dermatitis: a randomized, double‐blind trial. Dermatology 2010;221(1):71‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00769767; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- NCT00226707. Pimecrolimus cream 1% in patients (18 years of age and over) with mild to moderate chronic hand dermatitis. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00226707?term=hand+eczema&... (accessed 26 July 2017).
Jowkar 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Jowkar 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jowkar F, Saki N, Mokhtarpour A, Reza Saki M. Comparison of fumaric acid 5% cream versus triamcinolone 0.1% cream in the treatment of hand eczema. Acta Medica Iranica 2014;52(7):528‐31. [CENTRAL: CN‐00999261; PUBMED: 25135262] - PubMed
Kaaber 1983 {published data only}
-
- Kaaber K, Menné T, Veien N, Hougaard P. Treatment of nickel dermatitis with Antabuse; a double blind study. Contact Dermatitis 1983;9(4):297‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00568885; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Katsarou 2012 {published data only}
-
- Katsarou A, Makris M, Papagiannaki K, Lagogianni E, Tagka A, Kalogeromitros D. Tacrolimus 0.1% vs mometasone furoate topical treatment in allergic contact hand eczema: a prospective randomized clinical study. European Journal of Dermatology 2012;22(2):192‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00880927; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kemper 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kemper MFP, Valk PGM, Arnold WP. Efficacy of coal tar paste vs betamethasone valerate ointment 0.1% in hand eczema [Effectiviteit van koolteerpasta versus betamethasonvaleraatzalf 0.1% bij handeczeem]. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Dermatologie en Venereologie 1998;8:289‐91. [CENTRAL: CN‐00602201]
King 1984 {published data only}
-
- King CM, Chalmers RJ. A double‐blind study of superficial radiotherapy in chronic palmar eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 1984;111(4):451‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00035777; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kircik 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kircik LH, Eastman WJ, Gwazdauskas J. A randomized, double‐blind phase 4 study of the efficacy and safety of ethanol‐free clobetasol propionate foam, 0.05%, vs vehicle foam in the treatment of chronic hand dermatitis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2013;12(3):328‐34. [CENTRAL: CN‐00876862] - PubMed
Krejci‐Manwaring 2008 {published data only}
-
- Krejci‐Manwaring J, McCarty MA, Camacho F, Manuel J, Hartle J, Fleischer A Jr, et al. Topical tacrolimus 0.1% improves symptoms of hand dermatitis in patients treated with a prednisone taper. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2008;7(7):643‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00650082; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kucharekova 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kucharekova M, Kerkhof PC, Valk PG. A randomized comparison of an emollient containing skin‐related lipids with a petrolatum‐based emollient as adjunct in the treatment of chronic hand dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis 2003;48(6):293‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00470538; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lauriola 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lauriola MM, Pigatto PD, Pedrelli VF. A single‐center, randomized, perspective, investigator blinded, controlled trial to examine efficacy and safety of a Furpalmate‐containing cream in comparison to topical corticosteroid in atopic dermatitis of hands of 40 adult patients. 20th Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Lisbon (Abstracts on CD‐ROM). Geneva, 2011.
Lindelöf 1987 {published data only}
-
- Lindelöf B, Wrangsjö K, Lidén S. A double‐blind study of Grenz ray therapy in chronic eczema of the hands. British Journal of Dermatology 1987;117(1):77‐80. [CENTRAL: CN‐00050016; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lodén 2012a {published data only}
-
- Lodén M, Wirén K, Smerud KT, Meland N, Hønnås H, Mørk C, et al. The effect of a corticosteroid cream and a barrier‐strengthening moisturizer in hand eczema. A double‐blind, randomized, prospective, parallel group clinical trial. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology 2012;26(5):597‐601. [CENTRAL: CN‐00882835; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Möller 1983 {published data only}
-
- Möller H, Svartholm H, Dahl G. Intermittent maintenance therapy in chronic hand eczema with clobetasol propionate and flupredniden acetate. Current Medical Research & Opinion 1983;8(9):640‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00307918; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NCT01231854 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01231854. Ciclosporin versus alitretinoin for severe atopic hand dermatitis (TocyDD). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01231854 (accessed 27 February 2013).
Odia 1996 {published data only}
-
- Odia S, Vocks E, Rakoski J, Ring J. Successful treatment of dyshidrotic hand eczema using tap water iontophoresis with pulsed direct current. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1996;76(6):472‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00179694; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pacor 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pacor ML, Lorenzo G, Martinelli N, Mansueto P, Friso S, Pellitteri ME, et al. Tacrolimus ointment in nickel sulphate‐induced steroid‐resistant allergic contact dermatitis. Allergy & Asthma Proceedings 2006;27(6):527‐31. [CENTRAL: CN‐00574561; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pigatto 1990 {published data only}
-
- Pigatto PD, Gibelli E, Fumagalli M, Bigardi A, Morelli M, Altomare GF. Disodium cromoglycate versus diet in the treatment and prevention of nickel‐positive pompholyx. Contact Dermatitis 1990;22(1):27‐31. [CENTRAL: CN‐00568540; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Polderman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Polderman MC, Govaert JC, Cessie S, Pavel S. A double blind placebo‐controlled trial of UVA‐1 in the treatment of dyshidrotic eczema. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 2003;28(6):584‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00458902; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ruzicka 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Larsen F, Galewicz, Ruzicka T, Horváth A, Coenraads PJ, Zouboulis CC, et al. BAL40/9 (alitretinoin, 9‐cisretinoic acid) is effective and well tolerated in the treatment of refractory hand dermatitis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2003; Vol. 17:158. [Larsen 2003]
-
- Ruzicka T, Larsen FG, Galewicz D, Horváth A, Coenraads PJ, Thestrup‐Pedersen K, et al. Oral alitretinoin (9‐cis‐retinoic acid) therapy for chronic hand dermatitis in patients refractory to standard therapy. Results of a randomized, double‐blind placebo‐controlled, multicenter trial. Archives of Dermatology 2004;140(12):1453‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00503534; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ruzicka 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ruzicka T, Lynde CW, Jemec GB, Diepgen T, Berth‐Jones J, Coenraads PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral alitretinoin (9‐cis retinoic acid) in patients with severe chronic hand eczema refractory to topical corticosteroids: results of a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicentre trial. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;158(4):808‐17. [CENTRAL: CN‐00637962; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Said 2010 {published data only}
-
- Said NH, Lim KS, Chong WS, Theng CTS. A comparative study of UVA‐1 phototherapy versus betamethasone valerate 0.1% cream for chronic vesicular hand eczema. Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore 2011;40(11 Suppl 1):S28. [CENTRAL: CN‐01074005]
-
- Said NH, Lim KS, Chong WS, Theng CTS. A comparative study of ultraviolet light a1 phototherapy versus betamethasone valerate 0.1% cream for chronic vesicular hand eczema. Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore 2010;39(11 Suppl 1):S354. [CENTRAL: CN‐01074020]
Schnopp 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Schnopp C, Remling R, Möhrenschlager M, Weigl L, Ring J, Abeck D. Topical tacrolimus (FK506) and mometasone furoate in treatment of dyshidrotic palmar eczema: a randomized, observer‐blinded trial. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2002;46(1):73‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00376609; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sezer 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sezer E, Etikan I. Local narrowband UVB phototherapy vs. local PUVA in the treatment of chronic hand eczema. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 2007;23(1):10‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00577966; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sharma 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sharma AD. Disulfiram and low nickel diet in the management of hand eczema: a clinical study. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprology 2006;72(2):113‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00565442; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sheehan‐Dare 1989 {published data only}
-
- Sheehan‐Dare RA, Goodfield MJ, Rowell NR. Topical psoralen photochemotherapy (PUVA) and superficial radiotherapy in the treatment of chronic hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 1989;121(1):65‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00061541; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sjövall 1987 {published data only}
-
- Sjövall P, Christensen OB. Local and systemic effect of UVB irradiation in patients with chronic hand eczema. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1987;67(6):538‐41. [CENTRAL: CN‐00053072; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thestrup‐Pedersen 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Thestrup‐Pedersen K, Andersen KE, Menné T, Veien N. Treatment of hyperkeratotic dermatitis of the palms (eczema keratoticum) with oral acitretin. A single‐blind placebo controlled study. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 2001;81(5):353‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00377187; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tzaneva 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tzaneva S, Kittler H, Thallinger C, Hönigsmann H, Tanew A. Oral vs. bath PUVA using 8‐methoxypsoralen for chronic palmoplantar eczema. Photodermatolology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 2009;25(2):101‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00699561; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Uggeldahl 1986 {published data only}
-
- Uggeldahl PE, Kero M, Ulshagen K. Comparative effect of desonide cream 0.1% and 0.05% in patients with hand eczema. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1986;40(5):969‐73. [CENTRAL: CN‐00178392; EMBASE: 1987040454]
van Coevorden 2004a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Coevorden AM, Kamphof WG, Sonderen E, Bruynzeel DP, Coenraads PJ. Comparison of oral psoralen‐UV‐A with a portable tanning unit at home vs hospital administered bath psoralen‐UV‐A in patients with chronic hand eczema: an open‐label randomized controlled trial of efficacy. Archives of Dermatology 2004;140(12):1463‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00503535; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Veien 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Veien NK, Kaaber K, Larsen PO, Nielsen AO, Thestrup‐Pedersen K. Ranitidine treatment of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis: a double blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1995;32(6):1056‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00114123; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Veien 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Veien NK, Olholm Larsen P, Thestrup‐Pedersen K, Schou G. Long‐term, intermittent treatment of chronic hand eczema with mometasone furoate. British Journal of Dermatology 1999;140(5):882‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00278245; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Whitaker 1996 {published data only}
-
- Whitaker DK, Cilliers J, Beer C. Evening primrose oil (Epogam) in the treatment of chronic hand dermatitis: disappointing therapeutic results. Dermatology 1996;193(2):115‐20. [CENTRAL: CN‐00132445; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yousefi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yousefi M, Barikbin B, Kamalinejad M, Abolhasani E, Ebadi A, Younespour S, et al. Comparison of therapeutic effect of topical Nigella with Betamethasone and Eucerin in hand eczema. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2013;27(12):1498. [CENTRAL: CN‐00915004; DOI: 10.1111/jdv.12033] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aertgeerts 1985 {published data only}
-
- Aertgeerts P, Albring M, Klaschka F, Naseman T, Patzelt‐Wenczler R, Rauhut K, et al. Comparative testing of Kamillosan cream and steroidal (0.25% hydrocortisone, 0.75% fluocortin butyl ester) and non‐steroidal (5% bufexamac) dermatologic agents in maintenance therapy of eczematous diseases [Vergleichende Pruefung von Kamillosan Creme gegenueber steroidalen (0,25% hydrocortison, 0,75% fluorocortolon)]. Zeitschrift fur Hautkrankheiten 1985;60(3):270‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Berndt 2001 {published data only}
-
- Berndt U, Wigger‐Alberti W, Gabard B, Elsner P. Comparison of a barrier cream and its constituents on efficacy in occupational irritant hand eczema in nurses [Vergleich einer Hautschutzcreme und ihrer Grundlage bezuglich Wirksamkeit gegen das berufsbedingte irritative handekzem bei Krankenschwestern: eine anwendungsuntersuchung]. Dermatosen in Beruf und Umwelt. Occupation and Environment 2001;49(1A):77‐80. [CENTRAL: CN‐00441979; EMBASE: 2001126306]
Chen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chen Cz, Shu Xh, Yao L, Chu N. Treatment for 53 middle‐aged and old patients with chronic eczema of hand‐foot by spleen‐invigorating heat‐clearing method. Western Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2015;28(8):73‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐01434924]
Gergovska 2017 {published data only}
-
- Gergovska M, Briand E, Karp JM, Jacob SE, Vemula P, Gospodinov D, et al. Metal sequestering dermal cream exhibits beneficial effects in patients with dyshidrotic eczema associated with nickel induced allergic contact dermatitis ‐ a pilot study. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2017;72:310. [CENTRAL: CN‐01417582]
Grivcheva‐Panovska 2013 {published data only}
-
- Grivcheva‐Panovska V. Staphylococcus aureus and hand eczema: to treat or not to treat. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2013;68:423‐4. [EMBASE: 71369118]
Güler Özden 2004 {published data only}
-
- Güler Özden M, Ilter N, Gürer MA. A new treatment choice for chronic hand dermatitis: 1% pimecrolimus cream. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2004;18 Suppl:268.
HogenEsch 1998 {published data only}
-
- HogenEsch AJ, Coenraads PJ. Thuisbehandeling van chronisch recidiverend handeczeem met orale PUVA‐therapie. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Dermatologie en Venereologie 1998;8:267‐8.
Petering 2004 {published data only}
-
- Petering H, Breuer C, Herbst R, Kapp A, Werfel T. Comparison of localized high‐dose UVA1 irradiation versus topical cream psoralen‐UVA for treatment of chronic vesicular dyshidrotic eczema. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2004;50(1):68‐72. [CENTRAL: CN‐00520456; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rosén 1987 {published data only}
-
- Rosén K, Mobacken H, Swanbeck G. Chronic eczematous dermatitis of the hands: a comparison of PUVA and UVB treatment. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1987;67(1):48‐54. [CENTRAL: CN‐00047378; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zeichner 2018 {published data only}
-
- Zeichner JA, Berson D, Donald A. The use of an over‐the‐counter hand cream with sweet almond oil for the treatment of hand dermatitis. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2018;17(1):78‐82. [CENTRAL: CN‐01451024] - PubMed
Zimmerman 1967 {published data only}
-
- Zimmerman EH. Betamethasone 17‐Valerate. A custom‐made topical corticosteroid. Archives of Dermatology 1967;95(5):514‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Beitner 1996 {published data only}
-
- Beitner H. Treatment of hand dermatosis: a comparative study of a topical glucocorticoid ointment vs solution occluded with a new thin hydrocolloid dressing. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1996;76(5):408‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00332682; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CTRI/2009/091/000212 {published data only}
-
- CTRI/2009/091/000212. To compare the efficacy and safety of Herbavate vs. the conventional steroid therapy in the management of hand dermatitis. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2009/091/000212 (accessed 20 February 2014).
Draelos 2000 {published data only}
-
- Draelos ZD. Hydrogel barrier/repair creams and contact dermatitis. American Journal of Contact Dermatitis 2000;11(4):222‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00329003; MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
English 1989 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- English JS, Bunker CB, Ruthven K, Dowd PM, Greaves MV. A double‐blind comparison of the efficacy of betametasone diproprionate cream twice daily versus once daily in the treatment of steroid responsive dermatoses. Clinical & Experimental Dermatology 1989;14(1):32‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
EUCTR2004‐002398‐22‐DE {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2004‐002398‐22‐DE. Double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study to investigate the efficacy and safety of IDEA‐070 (ketoprofen in Transfersome®) in different dermatological diseases ‐ IDEA‐070 in different dermatological diseases. apps.who.int/trialsearch/default.aspx (accessed 20 February 2014).
EUCTR2005‐005793‐75‐DE {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2005‐005793‐75‐DE. Evaluation of the efficacy of a topical formulation containing ASF‐1075 in the treatment of chronic hand dermatitis ‐ hand dermatitis. apps.who.int/trialsearch/trial.aspx?trialid=EUCTR2005‐005793‐75‐DE (accessed 27 February 2013).
EUCTR2008‐006148‐20‐DE {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2008‐006148‐20‐DE. A vehicle‐controlled, investigator‐blinded intraindividual comparison to evaluate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of Momegalen rich cream and ointment in patients with hand and foot eczema and mild to moderate psoriasis. apps.who.int/trialsearch/trial.aspx?trialid=EUCTR2008‐006148‐20‐DE (accessed 27 February 2013).
Goh 1999 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Goh CL, Lim JT, Leow YH, Ang CB, Kohar YM. The therapeutic efficacy of mometasone furoate cream 0.1% applied once daily vs clobetasol propionate cream 0.05% applied twice daily in chronic eczema. Singapore Medical Journal 1999;40(5):341‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Grundmann 1999 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann‐Kollmann M, Behrens S, Peter RU, Kerscher M. Treatment of severe recalcitrant dermatoses of the palms and soles with PUVA‐bath versus PUVA‐cream. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 1999;15(2):87‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Haddican 2014 {published data only}
-
- Haddican M, Linkner RV, Singer G, On SCJ, Gagliotti M, Goldenberg G. Retapamulin 1% ointment and clobetasol propionate 0.05% foam is more efficacious than vehicle ointment and clobetasol 0.05% propionate foam in the treatment of hand/foot dermatitis. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology 2014;7(7):32‐6. - PMC - PubMed
Handa 1988 {published data only}
-
- Handa F, Sharma PK, Guha A, Sharma SD. Alcometasone dipropionate 0.05% ointment versus hydrocortisone 1.0% ointment in eczema & other dermatoses. Indian Journal of Dermatology 1988;33(1):5‐8. [PUBMED: 3074045] - PubMed
IRCT201112018263N1 {unpublished data only}
-
- IRCT201112018263N1. Evaluating of clobetasol 0.05% and doxepine 5% cream vs clobetasol 0.05% and placebo in the treatment of moderate to severe hand eczema. apps.who.int/trialsearch/trial.aspx?trialid=IRCT201112018263N1 (accessed 27 February 2013).
IRCT201212303734N2 {published data only}
-
- IRCT201212303734N2. Evaluating of anti‐dry cream vs fluocinolone acetonide 0/o25% cream in treatment of hand eczema. www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=3734&number=2 (accessed 20 February 2014).
Lassus 1981 {published data only}
-
- Lassus A, Salde L. A double‐blind comparison of two topical steroids in psoriasis and eczemas: budesonide 0.025% ointment and betamethasone‐17‐valerate 0.1% ointment. Pharmatherapeutica 1981;2(10):668‐72. [EMBASE: 1982033894]
NCT00404196 {published data only}
-
- NCT00404196. LEO19123 cream in the treatment of hand eczema. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00404196 (accessed 27 February 2013).
NCT00614289 {published data only}
-
- NCT00614289. Novel topical treatment of hand dermatitis (eczema). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00614289?term=NCT00614289 (accessed 27 February 2013).
NCT00843466 {published data only}
-
- NCT00843466. Compatibility of a mild, moisturizing hand cleanser for patients with mild to moderate hand dermatitis. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00843466 and apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=NCT00843466 (accessed 20 February 2014).
NCT00867607 {published data only}
-
- NCT00867607. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of 21 days dermal application of MRX‐6 on mild to moderate contact dermatitis. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00867607 (accessed 27 February 2013).
NCT00890968 {published data only}
-
- NCT00890968. Safety and efficacy study of triamcinolone acetonide DuraPeel to treat hand dermatitis (TAC‐202). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00890968 (accessed 27 February 2013).
NCT01950494 {published data only}
-
- NCT01950494. A one month, randomized, two‐center, parallel‐group, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of FiteBac hand sanitizer TID vs emollient therapy in the management of hand dermatitis in adults. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01950494 (accessed on 19 February 2014).
References to ongoing studies
IRCT2014012916412N1 {published data only}
-
- IRCT2014012916412N1. Effect of topical pumpkin, traditional medicine products on chronic hand eczema. www.irct.ir/searchresult.php?id=16412&number=1 (accessed 7 April 2017).
IRCT2017070922965N10 {published data only}
-
- IRCT2017070922965N10. Effect of topical atorvastatin on hand eczema [Evaluating the effect of topical atorvastatin as adjuvant therapy in treatment of hand eczema]. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=IRCT2017070922965N10 (accessed 21 April 2018).
ISRCTN80206075 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN80206075. Comparison of alitretinoin with PUVA as the first line treatment in patients with severe chronic hand eczema: a randomised controlled trial. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN80206075?q=hand%20eczema&filters=&sort=&... (accessed 8 April 2017).
JPRN‐UMIN000003326 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000003326. A clinical trial to determine the effect of olopatadine on itching in hand eczema. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=JPRN‐UMIN000003326 (accessed 20 February 2014).
NCT02664805 {published data only}
-
- NCT02664805. A phase 2a, proof of concept trial, testing twice daily applications of LEO 124249 ointment in the treatment of chronic hand eczema. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02664805 (accessed 7 April 2017).
NCT03026907 {published data only}
-
- NCT03026907. Efficacy of oral alitretinoin versus oral azathioprine in patients with severe chronic non‐hyperkeratotic hand eczema. A randomized prospective open‐label trial with blinded outcome assessment. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03026907 (accessed 25 July 2017).
NCT03026946 {published data only}
-
- NCT03026946. Efficacy of oral alitretinoin versus oral cyclosporine in patients with severe recurrent vesicular hand eczema. A randomized prospective open‐label trial with blinded outcome assessment. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03026946 (accessed 7 April 2017). - PMC - PubMed
PACTR201704002194318 {published data only}
-
- PACTR201704002194318. Assessment of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of hand eczema. www.pactr.org/ATMWeb/appmanager/atm/atmregistry?dar=true&tNo=PACTR20... (accessed 21 April 2018).
Additional references
Agner 2008
-
- Agner T, Andersen KE, Brandao FM, Bruynzeel DP, Bruze M, Frosch P, et al. Hand eczema severity and quality of life: a cross‐sectional, multicentre study of hand eczema patients. Contact Dermatitis 2008;59(1):43‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ahluwalia 1998
Augustin 2016
-
- Augustin M, Thaçi D, Kamps A. Impact on quality of life of alitretinoin in severe chronic hand eczema: FUGETTA real‐world study. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2016;14(12):1261‐70. - PubMed
Basra 2008
-
- Basra MK, Fenech R, Gatt RM, Salek MS, Finlay AY. The Dermatology Life Quality Index 1994‐2007: a comprehensive review of validation data and clinical results. British Journal of Dermatology 2008;159(5):997‐1035. - PubMed
Basra 2015
-
- Basra MKA, Salek MS, Camilleri L, Sturkey R, Finlay AY. Determining the minimal clinically important difference and responsiveness of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): further data. Dermatology 2015;230(1):27‐33. - PubMed
Blair 2016
-
- Blair HA, Scott LJ. Alitretinoin: a review in severe chronic hand eczema. Drugs 2016;76(13):1271‐9. - PubMed
Charman 2005
-
- Charman CR, English JS. Getting to grips with hand eczema: measuring skin disease severity objectively. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(2):199‐201. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coenraads 1998
-
- Coenraads PJ, Diepgen TL. Risk for hand eczema in employees with past or present atopic dermatitis. International Archives of Occupational & Environmental Health 1998;71(1):7‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coenraads 2005
-
- Coenraads PJ, Walle H, Thestrup‐Pedersen K, Ruzicka T, Dreno B, Loge C, et al. Construction and validation of a photographic guide for assessing severity of chronic hand dermatitis. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(2):296‐301. [PUBMED: 15727642] - PubMed
Coenraads 2012
-
- Coenraads PJ. Hand eczema. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;367(19):1829‐37. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cvetkovski 2005
-
- Cvetkovski RS, Rothman KJ, Olsen J, Mathiesen B, Iversen L, Johansen JD, et al. Relation between diagnoses on severity, sick leave and loss of job among patients with occupational hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(1):93‐8. [PUBMED: 15656807] - PubMed
de Paulis 1992
-
- Paulis A, Stellato C, Cirillo R, Ciccarelli A, Oriente A, Marone G. Anti‐inflammatory effect of FK‐506 on human skin mast cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 1992;99:723‐8. - PubMed
Diepgen 2003
-
- Diepgen TL. Occupational skin‐disease data in Europe. International Archives of Occupational & Environmental Health 2003;76(5):331‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Diepgen 2007
-
- Diepgen TL, Agner T, Aberer W, Berth‐Jones J, Cambazard F, Elsner P, et al. Management of chronic hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 2007;57(4):203‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Diepgen 2009a
-
- Diepgen TL, Andersen KE, Brandao FM, Bruze M, Bruynzeel DP, Frosch P, et al. Hand eczema classification: a cross‐sectional, multicentre study of the aetiology and morphology of hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;160(2):353‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Diepgen 2009b
-
- Diepgen TL, Elsner P, Schliemann S, Fartasch M, Köllner A, Skudlik C, et al. Guideline on the management of hand eczema ICD‐10 Code: L20. L23. L24. L25. L30. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2009;7(Suppl 3):S1‐16. - PubMed
Diepgen 2012
-
- Diepgen TL, Pfarr E, Zimmermann T. Efficacy and tolerability of alitretinoin for chronic hand eczema under daily practice conditions: results of the TOCCATA open study comprising 680 patients. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 2012;92(3):251‐5. - PubMed
Drake 1996
-
- Drake LA, Dinehart SM, Farmer ER, Goltz RW, Graham GF, Hordinsky MK, et al. Guidelines of care for the use of topical glucocorticosteroids. American Academy of Dermatology. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1996;35(4):615‐9. [PUBMED: 8859293] - PubMed
English 2009
-
- English J, Aldridge R, Gawkrodger DJ, Kownacki S, Statham B, White JLM, et al. Consensus statement on the management of chronic hand eczema. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 2009;34(7):761‐9. [PUBMED: 19747339] - PubMed
Faergemann 1987
-
- Faergemann J, Larkö O. The effect of UV light on human skin microorganisms. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1987;67:69‐72. - PubMed
Finlay 1994
-
- Finlay AY, Khan GK. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 1994;19(3):210‐6. [PUBMED: 8033378] - PubMed
Fox 1873
GRADEPro [Computer program]
-
- Brozek JL, Oxman A, Schünemann HJ. GRADEpro GDT. Version 3.6.1. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
Grainge 2013
-
- Grainge M, Leonardi‐Bee J. Reviews of conditions with low event rates. CSG Annual Meeting 2013 2013; Vol. https://skin.cochrane.org/csg‐annual‐meeting‐2013.
GraphPad [Computer program]
-
- Motulsky H. GraphPad Prism. San Diego: GraphPad Software, 2018.
Hald 2009
-
- Hald M, Agner T, Blands J, Veien NK, Laurberg G, Avnstorp C, et al. Clinical severity and prognosis of hand eczema. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;160(6):1229‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Halpern 2000
-
- Halpern SM, Anstey AV, Dawe RS, Diffey BL, Farr PM, Ferguson J, et al. Guidelines for topical PUVA: a report of a workshop of the British Photodermatology Group. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142(1):22‐31. [PUBMED: 10651690] - PubMed
Heede 2016
-
- Heede NG, Thyssen JP, Thuesen BH, Linneberg A, Johansen JD. Predictive factors of self‐reported hand eczema in adult Danes: a population‐based cohort study with 5‐year follow‐up. British Journal of Dermatology 2016;175(2):287‐95. [PUBMED: 26872425] - PubMed
Held 2005
-
- Held E, Skoet R, Johansen JD, Agner T. The hand eczema severity index (HECSI): a scoring system for clinical assessment of hand eczema. A study of inter and intraobserver reliability. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(2):302‐7. [PUBMED: 15727643] - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ. Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC, on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group and the Cochrane Bias Methods Group. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D, on behalf of the Cochrane Bias Methods Group. Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011d
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG, on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hönigsmann 2003
-
- Hönigsmann H. Mechanisms of phototherapy and photochemotherapy for photodermatoses. Dermatologic Therapy 2003;16(1):23‐7. - PubMed
Jekler 1990
-
- Jekler J, Larkö O. Combined UVA‐UVB versus UVB phototherapy for atopic dermatitis: a paired‐comparison study. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 1990;22:49‐53. - PubMed
Jensen 2006
-
- Jensen CS, Menné T, Johansen JD. Systemic contact dermatitis after oral exposure to nickel: a review with a modified meta‐analysis. Contact Dermatitis 2006;54(2):79‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johansen 2011
-
- Johansen JD, Hald M, Andersen BL, Laurberg G, Danielsen A, Avnstorp C, et al. Classification of hand eczema: clinical and aetiological types. Based on the guideline of the Danish Contact Dermatitis Group. Contact Dermatitis 2011;65(1):13‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kaae 2012
-
- Kaae J, Menné T, Carlsen BC, Zachariae C, Thyssen JP. The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss‐of‐function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype. Contact Dermatitis 2012;67(3):119‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kislat 2014
-
- Kislat A, Meller S, Mota R, Buhren BA, Gerber PA, Ruzicka T, et al. Alitretinoin, a dual RAR and RXR agonist, modulates leukocyte recruitment pathways and suppresses dendritic cell functions in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2014; Vol. 134:S72.
Kutzner 1986
-
- Kutzner H, Wurzel RM, Wolff HH. Are acrosyringia involved in the pathogenesis of "dyshidrosis"?. American Journal of Dermatopathology 1986;8(2):109‐16. [PUBMED: 2940934] - PubMed
Lodén 2010
-
- Lodén M, Wirén K, Smerud K, Meland N, Hønnås H, Mørk G, et al. Treatment with a barrier‐strengthening moisturizer prevents relapse of hand‐eczema. An open, randomized, prospective, parallel group study. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 2010;90(6):602‐6. [PUBMED: 21057743] - PubMed
Lodén 2012b
-
- Lodén M. Effect of moisturizers on epidermal barrier function. Clinics in Dermatology 2012;30(3):286‐96. - PubMed
Lynde 2010
-
- Lynde C, Guenther L, Diepgen TL, Sasseville D, Poulin Y, Gulliver W, et al. Canadian hand dermatitis management guidelines. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery 2010;14(6):267‐84. [PUBMED: 21084020] - PubMed
Majoie 2009
-
- Majoie IL, Oldhoff JM, Weelden H, Laaper‐Ertmann M, Bousema MT, Sigurdsson V, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B and medium‐dose ultraviolet A1 are equally effective in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009;60(1):77‐84. - PubMed
McLean 2013
Meding 1989
-
- Meding B, Swanbeck G. Epidemiology of different types of hand eczema in an industrial city. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1989;69(3):227‐33. [PUBMED: 2566226] - PubMed
Meding 1990
-
- Meding B, Swanbeck G. Predictive factors for hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 1990;23(3):154‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meding 2002
-
- Meding B, Järvholm B. Hand eczema in Swedish adults ‐ Changes in prevalence between 1983 and 1996. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2002;118(4):719‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meding 2004
-
- Meding B, Järvholm B. Incidence of hand eczema ‐ a population‐based retrospective study. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2004;122(4):873‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Meding 2005
-
- Meding B, Wrangsjo K, Jarvholm B. Fifteen‐year follow‐up of hand eczema: persistence and consequences. British Journal of Dermatology 2005;152(5):975‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Menné 2000
-
- Menné T, Maibach HI. Hand Eczema. 2nd Edition. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000:7, 158. [084937362X]
Menné 2011
-
- Menné T, Johansen JD, Sommerlund M, Veien NK, Danish Contact Dermatitis Group. Hand eczema guidelines based on the Danish guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 2011;65(1):3‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moberg 2009
-
- Moberg C, Alderling M, Meding B. Hand eczema and quality of life: a population‐based study. British Journal of Dermatology 2009;161(2):397‐403. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomised trials. Lancet 2001;357(9263):1191‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Molin 2015
-
- Molin S, Merl J, Dietrich KA, Regauer M, Flaig M, Letulé V, et al. The hand eczema proteome: imbalance of epidermal barrier proteins. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;172(4):994‐1001. [PUBMED: 25244099] - PubMed
Mollerup 2014
-
- Mollerup A, Veien NK, Johansen JD. An analysis of gender differences in patients with hand eczema ‐ everyday exposures, severity, and consequences. Contact Dermatitis 2014;71(1):21‐30. [PUBMED: 24618009 ] - PubMed
nationaleczema.org
-
- National Eczema Association. Eczema Treatment. www.nationaleczema.org/eczema/treatment/ (accessed 15 March 2019).
Nilsson 1985
-
- Nilsson E, Mikaelsson B, Andersson S. Atopy, occupation and domestic work as risk factors for hand eczema in hospital workers. Contact Dermatitis 1985;13(4):216‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Petersen 2014
-
- Petersen AH, Johansen JD, Hald M. Hand eczema ‐ prognosis and consequences: a 7‐year follow‐up study. British Journal of Dermatology 2014;171(6):1428‐33. [PUBMED: 25156938] - PubMed
Politiek 2016
-
- Politiek K, Oosterhaven JA, Vermeulen KM, Schuttelaar ML. Systematic review of cost‐of‐illness studies in hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 2016;75(2):67‐76. [PUBMED: 27218305] - PubMed
Rawlings 2004
-
- Rawlings AV, Harding CR. Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatologic Therapy 2004;17(Suppl 1):43‐8. - PubMed
RevMan [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ryan 2016
-
- Ryan R, Santesso N, Hill S. Preparing Summary of Findings (SoF) tables. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group. Version 1.0. cccrg.cochrane.org/author‐resources (accessed 26 July 2017).
Sakuma 2001
-
- Sakuma S, Higashi Y, Sato N, Sasakawa T, Sengoku T, Ohkubo Y, et al. Tacrolimus suppressed the production of cytokines involved in atopic dermatitis by direct stimulation of human PBMC system (comparison with steroids). International Immunopharmacology 2001;1:1219–26. - PubMed
Schleimer 1993
-
- Schleimer RP. An overview of glucocorticoid anti‐inflammatory actions. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1993;45(Suppl 1):S3‐7; discussion S43‐4. - PubMed
Schmitt 2010
-
- Schmitt J, Williams H, HOME Development Group. HOME Development Group. Harmonising Outcome Measures for Eczema (HOME). Report from the First International Consensus Meeting (HOME 1). British Journal of Dermatology 2010;163(6):1166‐8. [PUBMED: 21137114] - PubMed
Schmitt‐Hoffmann 2012
-
- Schmitt‐Hoffmann AH, Roos B, Schoetzau A, Leese PT, Meyer I, van de Wetering J, et al. Oral alitretinoin: a review of the clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Expert Reviews in Clinical Pharmacology 2012;5(4):373‐88. - PubMed
Schuttelaar 2013
-
- Schuttelaar ML, Coenraads PJ, Huizinga J, Monchy JG, Vermeulen KM. Increase in vesicular hand eczema after house dust mite inhalation provocation: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, cross‐over study. Contact Dermatitis 2013;68(2):76‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Simons 1997
-
- Simons JR, Bohnen IJ, Valk PG. A left‐right comparison of UVB phototherapy and topical photochemotherapy in bilateral chronic hand dermatitis after 6 weeks' treatment. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology 1997;22(1):7‐10. [PUBMED: 9330044] - PubMed
Soost 2012
-
- Soost S, Abdollahnia M, Kostev K, Worm M. Topical therapy of hand eczema ‐ analysis of the prescription profile from dermatologists in private practice. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft 2012;10(3):180‐4. [PUBMED: 21923729] - PubMed
Svensson 1988
-
- Svensson Å. Hand eczema: an evaluation of the frequency of atopic background and the difference in clinical pattern between patients with and without atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermato‐Venereologica 1988;68(6):509‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thyssen 2010
-
- Thyssen JP Johansen JD, Linneberg A, Menné T. The epidemiology of hand eczema in the general population ‐ prevalence and main findings. Contact Dermatitis 2010;62(2):75‐87. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
van Coevorden 2004b
-
- Coevorden AM, Coenraads PJ, Svensson A, Bavinck JN, Diepgen TL, Naldi L, et al. Overview of studies of treatments for hand eczema ‐ the EDEN hand eczema survey. British Journal of Dermatology 2004;151(2):446‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
van Coevorden 2006
-
- Coevorden AM, Sonderen E, Bouma J, Coenraads PJ. Assessment of severity of hand eczema: discrepancies between patient‐ and physician‐rated scores. British Journal of Dermatology 2006;155(6):1217‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
van den Bogaard 2013
Van Der Valk 2013
-
- Valk PG, Gils RF, Boot CR, Evers AW, Donders R, Alkemade HA, et al. A simple tool with which to study the course of chronic hand eczema in clinical practice: a reduced‐item score. Contact Dermatitis 2013;69(2):112‐7. [PUBMED: 23869731 ] - PubMed
Veien 2003
-
- Veien NK, Menne T. Treatment of hand eczema. Skin Therapy Letters 2003;8(5):4‐7. [PUBMED: 12910323] - PubMed
Veien 2008
-
- Veien NK, Hattel T, Laurberg G. Hand eczema: causes, course and prognosis II. Contact Dermatitis 2008;58(6):335‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Veien 2009
-
- Veien NK. Acute and recurrent vesicular hand dermatitis. Dermatologic Clinics 2009;27(3):337‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wallenhammar 2004
-
- Wallenhammar LM, Nyfjäll M, Lindberg M, Meding B. Health related quality of life and hand eczema ‐ a comparison of two instruments, including factor analysis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 2004;122(6):1381‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Weistenhöfer 2010
-
- Weistenhöfer W, Baumeister T, Drexler H, Kütting B. An overview of skin scores used for quantifying hand eczema: a critical update according to the criteria of evidence‐based medicine. British Journal of Dermatology 2010;162(2):239‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yngveson 2000
-
- Yngveson M, Svensson Å, Johannisson A, Isacsson Å. Hand dermatosis in upper secondary school pupils: 2‐year comparison and follow‐up. British Journal of Dermatology 2000;142(3):485‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

