Transduction of the Geomagnetic Field as Evidenced from alpha-Band Activity in the Human Brain
- PMID: 31028046
- PMCID: PMC6494972
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0483-18.2019
Transduction of the Geomagnetic Field as Evidenced from alpha-Band Activity in the Human Brain
Abstract
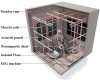
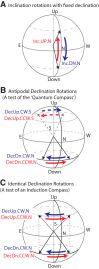
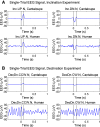
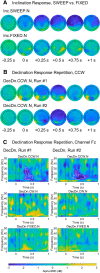
Magnetoreception, the perception of the geomagnetic field, is a sensory modality well-established across all major groups of vertebrates and some invertebrates, but its presence in humans has been tested rarely, yielding inconclusive results. We report here a strong, specific human brain response to ecologically-relevant rotations of Earth-strength magnetic fields. Following geomagnetic stimulation, a drop in amplitude of electroencephalography (EEG) alpha-oscillations (8-13 Hz) occurred in a repeatable manner. Termed alpha-event-related desynchronization (alpha-ERD), such a response has been associated previously with sensory and cognitive processing of external stimuli including vision, auditory and somatosensory cues. Alpha-ERD in response to the geomagnetic field was triggered only by horizontal rotations when the static vertical magnetic field was directed downwards, as it is in the Northern Hemisphere; no brain responses were elicited by the same horizontal rotations when the static vertical component was directed upwards. This implicates a biological response tuned to the ecology of the local human population, rather than a generic physical effect. Biophysical tests showed that the neural response was sensitive to static components of the magnetic field. This rules out all forms of electrical induction (including artifacts from the electrodes) which are determined solely on dynamic components of the field. The neural response was also sensitive to the polarity of the magnetic field. This rules out free-radical "quantum compass" mechanisms like the cryptochrome hypothesis, which can detect only axial alignment. Ferromagnetism remains a viable biophysical mechanism for sensory transduction and provides a basis to start the behavioral exploration of human magnetoreception.
Keywords: EEG; alpha-ERD; biogenic magnetite; biophysics; magnetoreception; quantum compass.
Copyright © 2019 Wang et al.
Figures


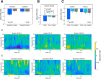
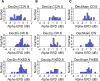
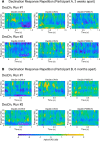
References
-
- Able KP, Gergits WF (1985) Human navigation: attempts to replicate Baker’s displacement experiment In: Magnetite biomineralization and magnetoreception in organisms: a new biomagnetism (Kirschvink JL, Jones DS, MacFadden BJ, eds), pp 569–572. New York, NY: Plenum Press.
-
- Baker RR (1980) Goal orientation by blindfolded humans after long-distance displacement: possible involvement of a magnetic sense. Science 210:555–557. - PubMed
-
- Baker RR (1982) Human navigation and the 6th sense. New York, NY: Simon and Schuster.
-
- Baker RR (1987) Human navigation and magnetoreception: the Manchester experiments do replicate. Animal Behav 35:691–704. 10.1016/S0003-3472(87)80105-7 - DOI
-
- Bazylinski DA, Schlezinger DR, Howes BH, Frankel RB, Epstein SS (2000) Occurrence and distribution of diverse populations of magnetic protists in a chemically stratified coastal salt pond. Chem Geol 169:319–328. 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00211-4 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
