Hit and run versus long-term activation of PARP-1 by its different domains fine-tunes nuclear processes
- PMID: 31028139
- PMCID: PMC6525528
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1901183116
Hit and run versus long-term activation of PARP-1 by its different domains fine-tunes nuclear processes
Abstract
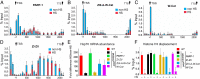
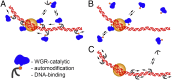
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) is a multidomain multifunctional nuclear enzyme involved in the regulation of the chromatin structure and transcription. PARP-1 consists of three functional domains: the N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) containing three zinc fingers, the automodification domain (A), and the C-terminal domain, which includes the protein interacting WGR domain (W) and the catalytic (Cat) subdomain responsible for the poly(ADP ribosyl)ating reaction. The mechanisms coordinating the functions of these domains and determining the positioning of PARP-1 in chromatin remain unknown. Using multiple deletional isoforms of PARP-1, lacking one or another of its three domains, as well as consisting of only one of those domains, we demonstrate that different functions of PARP-1 are coordinated by interactions among these domains and their targets. Interaction between the DBD and damaged DNA leads to a short-term binding and activation of PARP-1. This "hit and run" activation of PARP-1 initiates the DNA repair pathway at a specific point. The long-term chromatin loosening required to sustain transcription takes place when the C-terminal domain of PARP-1 binds to chromatin by interacting with histone H4 in the nucleosome. This long-term activation of PARP-1 results in a continuous accumulation of pADPr, which maintains chromatin in the loosened state around a certain locus so that the transcription machinery has continuous access to DNA. Cooperation between the DBD and C-terminal domain occurs in response to heat shock (HS), allowing PARP-1 to scan chromatin for specific binding sites.
Keywords: PARP-1; PARP-1 regulation; drosophila; poly(ADP-ribose); protein domains.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hobert O. Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science. 2008;319:1785–1786. - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Rajewsky N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Blais A, Dynlacht BD. Constructing transcriptional regulatory networks. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1499–1511. - PubMed
-
- Jaenisch R, Bird A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 2003;33:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Benabdallah NS, Bickmore WA. Regulatory domains and their mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2015;80:45–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

