Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ivosidenib, an oral, targeted inhibitor of mutant IDH1, in patients with advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 31028664
- PMCID: PMC7066280
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-019-00771-x
Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ivosidenib, an oral, targeted inhibitor of mutant IDH1, in patients with advanced solid tumors
Abstract
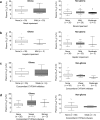
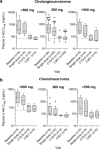
Background Mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1/IDH2) enzymes produce the oncometabolite D-2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG). Ivosidenib (AG-120) is a targeted mutant IDH1 inhibitor under evaluation in a phase 1 dose escalation and expansion study of IDH1-mutant advanced solid tumors including cholangiocarcinoma, chondrosarcoma, and glioma. We explored the pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) profiles of ivosidenib in these populations. Methods Ivosidenib was administered orally once (QD) or twice (BID) daily in continuous 28-day cycles; 168 patients received ≥1 dose within the range 100 mg BID to 1200 mg QD. PK and PD were assessed using validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assays. Results Ivosidenib demonstrated good oral exposure after single and multiple doses, was rapidly absorbed, and had a long terminal half-life (mean 40-102 h after single dose). Exposure increased less than dose proportionally. Steady state was reached by day 15, with moderate accumulation across all tumors (1.5- to 1.7-fold for area-under-the-curve at 500 mg QD). None of the intrinsic and extrinsic factors assessed affected ivosidenib exposure, including patient/disease characteristics and concomitant administration of weak CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers. After multiple doses in patients with cholangiocarcinoma or chondrosarcoma, plasma 2-HG was reduced by up to 98%, to levels seen in healthy subjects. Exposure-response relationships for safety and efficacy outcomes were flat across the doses tested. Conclusions Ivosidenib demonstrated good oral exposure and a long half-life. Robust, persistent plasma 2-HG inhibition was observed in IDH1-mutant cholangiocarcinoma and chondrosarcoma. Ivosidenib 500 mg QD is an appropriate dose irrespective of various intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Trial RegistrationClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02073994).
Keywords: 2-hydroxyglutarate; Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 inhibitor; Ivosidenib; Pharmacodynamics; Pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
B. Fan, S.S. Pandya, E. Manyak, L. Jiang, G. Liu, T. Nimkar, C. Gliser, M. Prahl Judge, and H. Yang are employees and stockholders of Agios. S. Agresta and D. Dai were employees and stockholders of Agios at the time of the study. E. Manyak was an employee of Agios at the time of the study and current stockholder of Agios. I.K. Mellinghoff has received research funding from General Electric, Amgen, and Lilly; has advisory roles with Agios, Puma Biotechnology, and Debiopharm Group; and has received an honorarium from Roche for a presentation. P.Y. Wen has participated in advisory boards for Abbvie, Agios, AstraZeneca, Blue Earth Diagnostics, Eli Lilly, Genentech/Roche, Immunomic Therapeutics, Kadmon, Kiyatec, Puma, Vascular Biogenics, Taiho, Deciphera, and VBI Vaccines; has acted as speaker for Merck and Prime Oncology; has received research support from Agios, AstraZeneca, Beigene, Eli Lily, Genentech/Roche, Karyopharm, Kazia, MediciNova, Merck, Novartis, Oncoceutics, Sanofi-Aventis, and VBI Vaccines. M.A. Lowery is a consultant and advisory board member for Agios and an advisory board member for Celgene, EMD Serono, and Roche. L. Goyal is an advisory board member for Pieris Pharmaceuticals and Debiopharm. W.D. Tap has received clinical trial funding from Agios during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Novartis, Eisai, Janssen, Immune Design, Adaptimmune, Daiichi Sankyo, Blueprint, Loxo, GlaxoSmithKline, Agios, and Plexxikon; holds a patent for Companion Diagnostic for CDK4 inhibitors - 14/854,329 pending to MSKCC/SKI; a patent for Methods of Treating Metastatic Sarcoma Using Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-Vec) and Pembrolizumab Combination Therapy - 62/671,625 pending to MSKCC/SKI; is a scientific advisory board member and stock owner for Certis Oncology Solutions and Atropos Therapeutics.
Figures



References
-
- Dang L, White DW, Gross S, Bennett BD, Bittinger MA, Driggers EM, Fantin VR, Jang HG, Jin S, Keenan MC, Marks KM, Prins RM, Ward PS, Yen KE, Liau LM, Rabinowitz JD, Cantley LC, Thompson CB, Vander Heiden MG, Su SM. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate. Nature. 2009;462:739–744. doi: 10.1038/nature08617. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ward PS, Patel J, Wise DR, Abdel-Wahab O, Bennett BD, Coller HA, Cross JR, Fantin VR, Hedvat CV, Perl AE, Rabinowitz JD, Carroll M, Su SM, Sharp KA, Levine RL, Thompson CB. The common feature of leukemia-associated IDH1 and IDH2 mutations is a neomorphic enzyme activity converting alpha-ketoglutarate to 2-hydroxyglutarate. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:225–234. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.01.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu C, Ward PS, Kapoor GS, Rohle D, Turcan S, Abdel-Wahab O, Edwards CR, Khanin R, Figueroa ME, Melnick A, Wellen KE, O'Rourke DM, Berger SL, Chan TA, Levine RL, Mellinghoff IK, Thompson CB. IDH mutation impairs histone demethylation and results in a block to cell differentiation. Nature. 2012;483:474–478. doi: 10.1038/nature10860. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saha SK, Parachoniak CA, Ghanta KS, Fitamant J, Ross KN, Najem MS, Gurumurthy S, Akbay EA, Sia D, Cornella H, Miltiadous O, Walesky C, Deshpande V, Zhu AX, Hezel AF, Yen KE, Straley KS, Travins J, Popovici-Muller J, Gliser C, Ferrone CR, Apte U, Llovet JM, Wong KK, Ramaswamy S, Bardeesy N. Mutant IDH inhibits HNF-4α to block hepatocyte differentiation and promote biliary cancer. Nature. 2014;513:110–114. doi: 10.1038/nature13441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu W, Yang H, Liu Y, Yang Y, Wang P, Kim SH, Ito S, Yang C, Wang P, Xiao MT, Liu LX, Jiang WQ, Liu J, Zhang JY, Wang B, Frye S, Zhang Y, Xu YH, Lei QY, Guan KL, Zhao SM, Xiong Y. Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate is a competitive inhibitor of α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:17–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.12.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

