Reductions in GABA following a tDCS-language intervention for primary progressive aphasia
- PMID: 31029018
- PMCID: PMC6591063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.03.011
Reductions in GABA following a tDCS-language intervention for primary progressive aphasia
Abstract
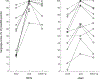
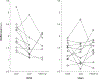
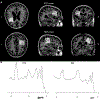
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) has shown efficacy in augmenting the effects of language therapy in primary progressive aphasia (PPA). The mechanism of action of tDCS is not understood, but preliminary work in healthy adults suggests it modulates γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels to create an environment optimal for learning. It is unknown if this proposed mechanism translates to aging or neurodegenerative conditions. This study tested the hypothesis that tDCS reduces GABA at the stimulated tissue in PPA. We applied GABA-edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy to quantify GABA levels before and after a sham-controlled tDCS intervention with language therapy in PPA. All participants showed improvements but those receiving active tDCS showed significantly greater language improvements compared to sham both immediately after the intervention and at 2-month follow-up. GABA levels in the targeted tissue decreased from baseline after the intervention and remained decreased 2 months after the intervention. This work supports the hypothesis that tDCS modulates GABAergic inhibition to augment learning and is clinically useful for PPA combined with language therapy.
Keywords: Anodal tDCS; GABA-edited MRS; Language therapy; Learning; Neural plasticity; Neurodegenerative disorder.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the subject matter of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Buch ER, Santarnecchi E, Antal A, Born J, Celnik PA, Classen J, Gerloff C, Hallett M, Hummel FC, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A, Paulus WJ, Reis J, Robertson EM, Rothwell JC, Sandrini M, Schambra HM, Wassermann EM, Ziemann U, Cohen LG, 2017. Effects of tDCS on motor learning and memory formation: A consensus and critical position paper. Clin Neurophysiol 128(4), 589–603. - PubMed
-
- Clark VP, Coffman BA, Trumbo MC, Gasparovic C, 2011. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) produces localized and specific alterations in neurochemistry: a (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neurosci Lett 500(1), 67–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

