CSESA: an R package to predict Salmonella enterica serotype based on newly incorporated spacer pairs of CRISPR
- PMID: 31029079
- PMCID: PMC6486994
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-2806-5
CSESA: an R package to predict Salmonella enterica serotype based on newly incorporated spacer pairs of CRISPR
Abstract
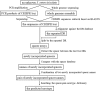
Background: Salmonella enterica is a major cause of bacterial food-borne disease worldwide. Immunological serotyping is the most commonly used typing method to characterize S. enterica isolates, but is time-consuming and requires expensive reagents. Here, we developed an R package CSESA (CRISPR-based Salmonella enterica Serotype Analyzer) to predict the serotype based on the CRISPR loci of S. enterica.
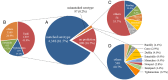
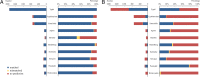
Results: CSESA has implemented the CRISPR typing method CLSPT and extended its coverage on diverse S. enterica serotypes. This package takes CRISPR sequences or the genome sequences as input and provides users with the predicted serotypes. CSESA has shown excellent performance with currently available sequences of S. enterica.
Conclusions: CSESA is a convenient and useful tool for the prediction of S. enterica serotypes. The application of CSESA package can improve the efficiency of serotyping for S. enterica and reduce the burden of manpower resources. CSESA is freely available from CRAN at https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/CSESA/ .
Keywords: CSESA; S. enterica; Serotyping.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat locus spacer pair typing method based on the newly incorporated spacer for Salmonella enterica.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Aug;52(8):2955-62. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00696-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24899040 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing analysis and CRISPR genotyping of rare antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from food and related sources.Food Microbiol. 2021 Feb;93:103601. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103601. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Food Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32912589
-
Genetic analysis of Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum biovar Pullorum based on characterization and evolution of CRISPR sequence.Vet Microbiol. 2017 May;203:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.02.010. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28619172
-
CRISPR Typing of Salmonella Isolates from Different Resources.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2182:45-50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0791-6_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32894486
-
Novel virulence gene and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) multilocus sequence typing scheme for subtyping of the major serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Mar;77(6):1946-56. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02625-10. Epub 2011 Jan 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21278266 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Typing methods based on whole genome sequencing data.One Health Outlook. 2020 Feb 18;2:3. doi: 10.1186/s42522-020-0010-1. eCollection 2020. One Health Outlook. 2020. PMID: 33829127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, O’Brien SJ, et al. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:882–889. - PubMed
-
- Grimont P, Weill F. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars. 9. Paris, France: WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur; 2007.
-
- Chen Y, Brown E, Knabel S. Molecular epidemiology of foodborne pathogens. Genomics Foodborne Bact Pathog. 2011:403–53.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

