Central Amygdala Prepronociceptin-Expressing Neurons Mediate Palatable Food Consumption and Reward
- PMID: 31029403
- PMCID: PMC6750705
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.03.037
Central Amygdala Prepronociceptin-Expressing Neurons Mediate Palatable Food Consumption and Reward
Erratum in
-
Central Amygdala Prepronociceptin-Expressing Neurons Mediate Palatable Food Consumption and Reward.Neuron. 2019 Jun 5;102(5):1088. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.04.036. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31170393 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
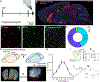
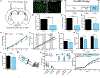
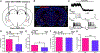
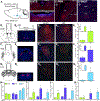
Food palatability is one of many factors that drives food consumption, and the hedonic drive to feed is a key contributor to obesity and binge eating. In this study, we identified a population of prepronociceptin-expressing cells in the central amygdala (PnocCeA) that are activated by palatable food consumption. Ablation or chemogenetic inhibition of these cells reduces palatable food consumption. Additionally, ablation of PnocCeA cells reduces high-fat-diet-driven increases in bodyweight and adiposity. PnocCeA neurons project to the ventral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (vBNST), parabrachial nucleus (PBN), and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS), and activation of cell bodies in the central amygdala (CeA) or axons in the vBNST, PBN, and NTS produces reward behavior but did not promote feeding of palatable food. These data suggest that the PnocCeA network is necessary for promoting the reinforcing and rewarding properties of palatable food, but activation of this network itself is not sufficient to promote feeding.
Keywords: binge eating; central amygdala; nociceptin; nucleus of the solitary tract; obesity; parabrachial nucleus; reward.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 AA023555/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AA000411/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH112355/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK115902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA011605/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AA023440/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH076694/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007431/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA034929/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA019454/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH105892/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020911/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

