Troponin structure and function: a view of recent progress
- PMID: 31030382
- PMCID: PMC7109197
- DOI: 10.1007/s10974-019-09513-1
Troponin structure and function: a view of recent progress
Abstract
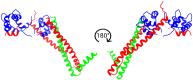
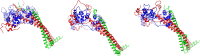
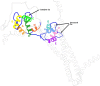
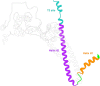
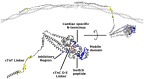
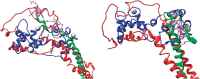
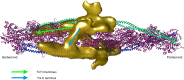
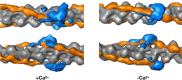
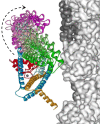
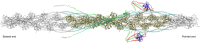
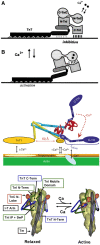
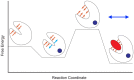
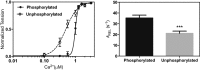
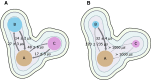
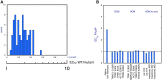
The molecular mechanism by which Ca2+ binding and phosphorylation regulate muscle contraction through Troponin is not yet fully understood. Revealing the differences between the relaxed and active structure of cTn, as well as the conformational changes that follow phosphorylation has remained a challenge for structural biologists over the years. Here we review the current understanding of how Ca2+, phosphorylation and disease-causing mutations affect the structure and dynamics of troponin to regulate the thin filament based on electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, NMR and molecular dynamics methodologies.
Keywords: Ca2+; Muscle regulation; Mutation; Phosphorylation; Thin filaments; Troponin.
Figures

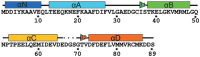





References
-
- Ayaz-Guner S, Zhang J, Li L, Walker JW, Ge Y. In vivo phosphorylation site mapping in mouse cardiac troponin i by high resolution top-down electron capture dissociation mass spectrometry: Ser22/23 are the only sites basally phosphorylated. Biochemistry. 2009;48:8161–8170. doi: 10.1021/bi900739f. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

