Hirschsprung disease in an adult with intestinal malrotation and volvulus: an exceptional association
- PMID: 31030669
- PMCID: PMC6487523
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-019-2020-0
Hirschsprung disease in an adult with intestinal malrotation and volvulus: an exceptional association
Abstract
Background: Hirschsprung disease is a neonatal discovery in almost all cases, and the association of Hirschsprung disease in adults with symptomatic intestinal malrotation is unusual. This combination delays diagnosis and can lead to mistake in surgical strategy.
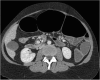
Case presentation: A 43-year-old patient with a history of colectomy for colonic inertia and megadolichocolon was admitted to the Carcassonne Hospital emergency room for a volvulus of small bowel obstruction in a chronic intestinal obstruction context with episodes of acute, variable-looking occlusive syndromes. Intestinal malrotation was discovered during surgical small bowel detorsion. The acute occlusion syndrome recurred after the procedure. In view of the unfavorable evolution, an emptying of the dilated small bowel and a discharge ileostomy upstream of the rectum were performed. In the face of postoperative improvement, rectal manometry and deep full parietal rectal biopsies made it possible to highlight the diagnosis of Hirschsprung disease. The patient thus had functional acute occlusive syndromes and chronic occlusion due to Hirschsprung disease of attenuated form and acute organic occlusive syndromes related to her incomplete common mesentery.
Conclusions: This rare association, which may be responsible for delayed diagnostic and therapeutic wandering, highlights the importance of performing manometry and deep full parietal biopsies before a colectomy for colonic inertia, as well as the possibility of suggesting a common Hirschsprung disease and/or mesentery in an adult with multiple occlusive syndromes of variable appearance.
Keywords: Adult Hirschsprung disease; Chronic occlusion; Constipation; Malrotation intestinal; Multiple occlusive syndrome; Small bowel volvulus.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The patient gave us her ethical approval.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Faucheron JL, Poncet G, Voirin D, Moreno W, Stathopoulos L. Maladie de Hirschsprung chez l’adulte. EMC Techn Chir Dig. 2009;4:1–9. doi: 10.1016/S0246-0424(09)43191-1. - DOI
-
- Tomita R, Ikeda T, Fujisaki S, Tanjoh K, Munakata K. Hirschsprung’s disease and its allied disorders in adults’ histological and clinical studies. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50(52):1050–1053. - PubMed
-
- Philippe-Chomette P, Aigrain Y. Diagnosis and management of Hirschsprung disease in child [in French] J Pédiatr Puéric. 2008;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jpp.2007.11.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

