Oral Pregabalin as Premedication on Anxiolysis and Stress Response to Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Double-Blind Study
- PMID: 31031488
- PMCID: PMC6444940
- DOI: 10.4103/aer.AER_12_19
Oral Pregabalin as Premedication on Anxiolysis and Stress Response to Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Double-Blind Study
Abstract
Background: Direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation lead to increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This can cause serious complications in patients with coronary artery disease, reactive airways, or intracranial neuropathology. Preoperative anxiety is associated with greater level of postoperative pain. Attenuation of anxiety and hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation are cornerstone of better anesthetic outcome. Gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) have been known to possess anxiolytic, analgesic, and anticonvulsant properties.
Aim: The aim of this study is to determine the effects of oral pregabalin on anxiolysis and attenuation of stress response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation.
Study design: This was a prospective randomized double-blind placebo controlled study.
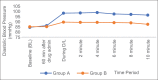
Materials and methods: A total of 60 patients ASA physical status Class I and II, undergoing elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy, were randomly allocated into two groups receiving either oral placebo or oral pregabalin 150 mg, 60 min before induction of anesthesia. Visual analog scale (VAS) for anxiety was recorded before, and 60 min after giving the drug. Hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and mean arterial pressure) were recorded before, and 60 min after giving drug, during and 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 min after intubation.
Results: During preinduction, pregabalin showed a decrease in VAS and attenuation of stress response to laryngoscopy and intubation compared to that of placebo. The premedicated patients were hemodynamically stable perioperatively without side effects.
Conclusion: Pregabalin is effective in attenuating preoperative anxiety and stress response to endotracheal intubation.
Keywords: Anxiolysis; endotracheal intubation; pregabalin; stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oral premedication with pregabalin or clonidine for hemodynamic stability during laryngoscopy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A comparative evaluation.Saudi J Anaesth. 2011 Apr;5(2):179-84. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.82791. Saudi J Anaesth. 2011. PMID: 21804800 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Clonidine vs Oral Pregabalin Premedication to Attenuate Pressor Response to Direct Laryngoscopy in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Randomized Double Blind Study.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Sep;10(9):UC21-UC25. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/19756.8513. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 27790557 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of Oral Gabapentin, Pregabalin, and Clonidine as Premedication for Anxiolysis, Sedation, and Attenuation of Pressor Response to Endotracheal Intubation.Anesth Essays Res. 2017 Jul-Sep;11(3):558-560. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_34_17. Anesth Essays Res. 2017. PMID: 28928547 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Low-dose and High-dose Pregabalin and Cardiovascular Response to Endotracheal Intubation: A Prospective, Randomized, Single-blind, Controlled Study in China.Clin Ther. 2019 Jan;41(1):68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 30553555 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Oral Clonidine and Gabapentin Premedication for Attenuation of Pressor Response to Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation.Anesth Essays Res. 2020 Jul-Sep;14(3):412-419. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_114_20. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Anesth Essays Res. 2020. PMID: 34092851 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Reduction of Acute Postoperative Pain With Pre-Emptive Pregabalin Following Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.Cureus. 2022 Aug 8;14(8):e27783. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27783. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36106290 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Dexmedetomidine and Pregabalin as Premedication Agent to Attenuate Adverse Hemodynamic and Stress Response in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.Anesth Essays Res. 2019 Oct-Dec;13(4):608-614. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_115_19. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Anesth Essays Res. 2019. PMID: 32009703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spielberger C. Vol. 1. New York: Academic Press; 1972. Anxiety as an emotional state. Anxiety: Current Trends in Theory and Research; pp. 1–19.
-
- Lamontagne LL, Hepworth JT, Salisbury MH. Anxiety and postoperative pain in children who undergo major orthopedic surgery. Appl Nurs Res. 2001;14:119–24. - PubMed
-
- de Groot KI, Boeke S, van den Berge HJ, Duivenvoorden HJ, Bonke B, Passchier J, et al. The influence of psychological variables on postoperative anxiety and physical complaints in patients undergoing lumbar surgery. Pain. 1997;69:19–25. - PubMed
-
- Kain ZN, Mayes LC, Caldwell-Andrews AA, Karas DE, McClain BC. Preoperative anxiety, postoperative pain, and behavioral recovery in young children undergoing surgery. Pediatrics. 2006;118:651–8. - PubMed
-
- Kain ZN, Sevarino FB, Rinder C, Pincus S, Alexander GM, Ivy M, et al. Preoperative anxiolysis and postoperative recovery in women undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Anesthesiology. 2001;94:415–22. - PubMed

