Multiple Beneficial Effects of Ghrelin Agonist, HM01 on Homeostasis Alterations in 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson's Disease in Male Rats
- PMID: 31031602
- PMCID: PMC6474391
- DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2019.00013
Multiple Beneficial Effects of Ghrelin Agonist, HM01 on Homeostasis Alterations in 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson's Disease in Male Rats
Abstract
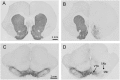
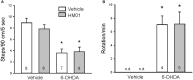
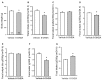
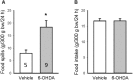
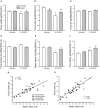
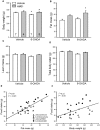
Background and objective: Developing therapy for non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD) is important for improving patients' quality of life. Previously, we reported that the ghrelin receptor agonist, HM01 normalized the decreased 4-h fecal output and levodopa-inhibited gastric emptying in 6-OHDA rats, and activated selective areas in brain and spinal cord. In this study, we evaluated whether chronic HM01 treatment influences motor functions and/or has beneficial effects on non-motor symptoms including alterations of body weight and composition, defecation, feeding and water intake in 6-OHDA rats. Methods: Male rats were microinjected unilaterally into the medial forebrain bundle with either vehicle or 6-OHDA. Three weeks later, we assessed basal body weight, and 24-h fecal output (pellets, weight, dry weight and water content), water intake and food intake (ingested and spillage). Then, HM01 (3 mg/kg) or vehicle was given per gavage daily for 10-12 days and the same parameters were re-assessed daily. Motor behavior (stepping and rotations tests), body composition were monitored before and after the HM01 treatment. Results: 6-OHDA rats showed motor deficits in rotation test induced by apomorphine and stepping test. They also displayed a significant reduction in body weight, water consumption, fecal weight and water content and an increase in food spillage compared to vehicle microinjected rats. Daily oral treatment of HM01 did not modify motor alterations compared to vehicle but significantly increased the body weight, fat mass, and 24-h fecal weight, fecal water content, food and water intake in 6-OHDA rats, while HM01 had no significant effect in vehicle microinjected rats. Fecal weight and water content were both correlated with water intake, but not with food intake. Fat mass, but not body weight, was correlated with food intake. HM01 effects were significant after 24 h and remained similar during the treatment. Conclusions: Chronic treatment with ghrelin agonist, HM01 improved several non-motor symptoms in the rat PD model induced by 6-OHDA lesion including the decrease in body weight, water consumption, fecal weight and water content, and increased food intake while not improving the motor deficits. These findings provide pre-clinical evidence of potential benefits of ghrelin agonists to alleviate non-motor symptoms in PD patients.
Keywords: 6-hydroxydopamine; body composition; defecation; ghrelin agonist; rat; water intake.
Figures