Plant-Derived Alkaloids: The Promising Disease-Modifying Agents for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 31031622
- PMCID: PMC6473079
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00351
Plant-Derived Alkaloids: The Promising Disease-Modifying Agents for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
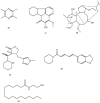
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) represents a group of intestinal disorders with self-destructive and chronic inflammation in the digestive tract, requiring long-term medications. However, as many side effects and drug resistance are frequently encountered, safer and more effective agents for IBD treatment are urgently needed. Over the past few decades, a variety of natural alkaloids made of plants or medicinal herbs have attracted considerable interest because of the excellent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; additionally, these alkaloids have been reported to reduce the colonic inflammation and damage in a range of colitic models. In this review paper, we summarize the recent findings regarding the anti-colitis activity of plant-derived alkaloids and emphasize their therapeutic potential for the treatment of IBD; obvious improvement of the colonic oxidative and pro-inflammatory status, significant preservation of the epithelial barrier function and positive modulation of the gut microbiota are the underlying mechanisms for the plant-derived alkaloids to treat IBD. Further clinical trials and preclinical studies to unravel the molecular mechanism are essential to promote the clinical translation of plant-derived alkaloids for IBD.
Keywords: action mechanism; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease; plant-derived alkaloids; therapeutic effects.
Figures
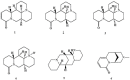
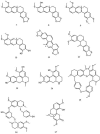
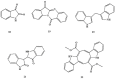
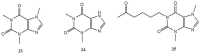
References
-
- Ashihara H., Mizuno K., Yokota T., Crozier A. (2017). “Xanthine alkaloids: occurrence, biosynthesis, and function in plants,” in Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 105 eds Kinghorn A. D., Falk H., Gibbons S., Kobayashi J. I. (Cham: Springer International Publishing; ) 1–88. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

