Connecting Metainflammation and Neuroinflammation Through the PTN-MK-RPTPβ/ζ Axis: Relevance in Therapeutic Development
- PMID: 31031625
- PMCID: PMC6474308
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00377
Connecting Metainflammation and Neuroinflammation Through the PTN-MK-RPTPβ/ζ Axis: Relevance in Therapeutic Development
Abstract
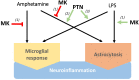
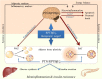
Inflammation is a common factor of pathologies such as obesity, type 2 diabetes or neurodegenerative diseases. Chronic inflammation is considered part of the pathogenic mechanisms of different disorders associated with aging. Interestingly, peripheral inflammation and the associated metabolic alterations not only facilitate insulin resistance and diabetes but also neurodegenerative disorders. Therefore, the identification of novel pathways, common to the development of these diseases, which modulate the immune response and signaling is key. It will provide highly relevant information to advance our knowledge of the multifactorial process of aging, and to establish new biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets to counteract the underlying chronic inflammatory processes. One novel pathway that regulates peripheral and central immune responses is triggered by the cytokines pleiotrophin (PTN) and midkine (MK), which bind its receptor, Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (RPTP) β/ζ, and inactivate its phosphatase activity. In this review, we compile a growing body of knowledge suggesting that PTN and MK modulate the immune response and/or inflammation in different pathologies characterized by peripheral inflammation associated with insulin resistance, such as aging, and in central disorders characterized by overt neuroinflammation, such as neurodegenerative diseases and endotoxemia. Evidence strongly suggests that regulation of the PTN and MK signaling pathways may provide new therapeutic opportunities particularly in those neurological disorders characterized by increased PTN and/or MK cerebral levels and neuroinflammation. Importantly, we discuss existing therapeutics, and others being developed, that modulate these signaling pathways, and their potential use in pathologies characterized by overt neuroinflammation.
Keywords: PTPRZ; aging; inflammation; midkine; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; obesity; pleiotrophin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute Morphine, Chronic Morphine, and Morphine Withdrawal Differently Affect Pleiotrophin, Midkine, and Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase β/ζ Regulation in the Ventral Tegmental Area.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):495-510. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9631-2. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26742526
-
Role of Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase β/ζ in Neuron-Microglia Communication in a Cellular Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 22;22(13):6646. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136646. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206170 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic analysis of the striatum from pleiotrophin knockout and midkine knockout mice treated with cocaine reveals regulation of oxidative stress-related proteins potentially underlying cocaine-induced neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration.Toxicology. 2013 Dec 6;314(1):166-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2013.09.014. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Toxicology. 2013. PMID: 24096156
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: "Ligand Independent Activation" mediated by the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ signaling pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2219-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23777859 Review.
-
Functional receptors and intracellular signal pathways of midkine (MK) and pleiotrophin (PTN).Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(4):511-20. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b13-00845. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014. PMID: 24694599 Review.
Cited by
-
Constitutive Pleiotrophin Deletion Results in a Phenotype with an Altered Pancreatic Morphology and Function in Old Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10960. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010960. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456743 Free PMC article.
-
NMR Characterization of the Interactions Between Glycosaminoglycans and Proteins.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 16;8:646808. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.646808. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33796549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of miR-137 in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 30;25(13):7229. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137229. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid immunological cytokines predict intracranial tumor response to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases.Oncoimmunology. 2023 Dec 7;13(1):2290790. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2290790. eCollection 2024. Oncoimmunology. 2023. PMID: 38169917 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotrophin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Possible Treatment for Osteoporosis.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 16;15(2):658. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020658. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bluher M., Bashan N., Shai I., Harman-Boehm I., Tarnovscki T., Avinaoch E., et al. (2009). Activated Ask1-MKK4-p38MAPK/JNK stress signaling pathway in human omental fat tissue may link macrophage infiltration to whole-body Insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94 2507–2515. 10.1210/jc.2009-0002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

