Impact of Psychotherapy in Psychosis: A Retrospective Case Control Study
- PMID: 31031656
- PMCID: PMC6470395
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00204
Impact of Psychotherapy in Psychosis: A Retrospective Case Control Study
Abstract
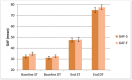
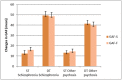
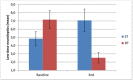
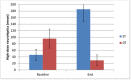
Background: The need for psychological therapies for psychosis has become apparent since long-term antipsychotic drug treatment has a range of adverse side effects, with moderate therapeutic effects at best. Aims: To investigate whether the psychotherapeutic approach, dialogue therapy (DT) is associated with improvements of symptoms and functioning beyond standard psychiatric treatment (ST) in both schizophrenia and other psychosis. Methods: A retrospective case-control design, comparing 54 patients with different psychoses who received DT with 54 patients in a control group receiving ST was carried out. The groups were matched on diagnosis, age, sex, and treatment start. Outcome measures were Global assessment of functioning (GAF) scores, medications at follow up, and hospital stays after completed outpatient treatment. Results: Mean time in treatment from inclusion to follow-up was 3 years and 5 months. At follow-up, GAF functioning (GAF-F) and GAF symptom (GAF-S) scores both were significantly higher in the DT group than the ST group. Effect sizes (Cohen's d) were large; 1.8 for GAF-S and 2.1 for GAF-F. At follow-up, the use of psychoactive drugs was significantly reduced despite a shorter time in psychotherapy in the DT group compared to the ST group. Days of hospitalizations after end of treatment in the study period were significantly reduced in both groups compared to the period before start of treatment. Conclusions: The findings from this exploratory study are consistent with the possibility that dialogue therapy may lead to improvements in symptoms and functioning compared to standard treatment in psychosis.
Keywords: antipsychotic medication; dialogue therapy; global assessment of functioning; psychosis; psychotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traumatized refugees: morbidity, treatment and predictors of outcome.Dan Med J. 2014 Aug;61(8):B4871. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25162447 Review.
-
Supportive psychodynamic psychotherapy versus treatment as usual for first-episode psychosis: two-year outcome.Psychiatry. 2012 Winter;75(4):331-41. doi: 10.1521/psyc.2012.75.4.331. Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23244011 Clinical Trial.
-
Misdiagnosis, duration of untreated illness (DUI) and outcome in bipolar patients with psychotic symptoms: A naturalistic study.J Affect Disord. 2015 Aug 15;182:70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.04.024. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Affect Disord. 2015. PMID: 25978716
-
Association between Global Assessment of Functioning scores and indicators of functioning, severity, and prognosis in first-time schizophrenia.Clin Epidemiol. 2016 Sep 2;8:323-32. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S109036. eCollection 2016. Clin Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 27660490 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcome of cognitive behaviour therapy clinical trials in central Scotland.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Nov;9(42):1-174. doi: 10.3310/hta9420. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 16266559 Review.
Cited by
-
A tablet-based quantitative assessment of manual dexterity for detection of early psychosis.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jun 26;14:1200864. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1200864. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37435404 Free PMC article.
-
A Treatment Model for Young Adults with Severe Mental Disorders in a Community Mental Health Center: The Crisalide Project and the Potential Space.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 18;19(22):15252. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192215252. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo X, Zhai J, Liu Z, Fang M, Wang B, Wang C, et al. . Effect of antipsychotic medication alone vs. combined with psychosocial intervention on outcomes of early-stage schizophrenia: a randomized, 1-year study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2010) 67:895–904. 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams P. Rethinking Madness: Towards a Paradigm Shift in Our Understanding and Treatment of Psychosis. San Francisco, CA: Sky's Edge Publishing; (2012).
-
- Geekie J. (ed). Experiencing Psychosis: Personal and Professional Perspectives. London: Routledge; (2012).
-
- Gleeson JFM, Killackey E, Krstev H. (eds). Psychotherapies for the psychoses: theoretical, cultural and clinical integration. London: Routledge; (2008).
-
- NICE Psychosis and Schizophrenia in Adults: Treatment and Management: Updated Edition 2014. Clinical Guideline 178. London: NICE; (2014).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

