Potent Fc Receptor Signaling by IgA Leads to Superior Killing of Cancer Cells by Neutrophils Compared to IgG
- PMID: 31031746
- PMCID: PMC6470253
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00704
Potent Fc Receptor Signaling by IgA Leads to Superior Killing of Cancer Cells by Neutrophils Compared to IgG
Abstract
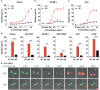
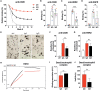
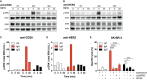
Antibody therapy of cancer is increasingly used in the clinic and has improved patient's life expectancy. Except for immune checkpoint inhibition, the mode of action of many antibodies is to recognize overexpressed or specific tumor antigens and initiate either direct F(ab')2-mediated tumor cell killing, or Fc-mediated effects such as complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity/phagocytosis (ADCC/P) after binding to activating Fc receptors. All antibodies used in the clinic are of the IgG isotype. The IgA isotype can, however, also elicit powerful anti-tumor responses through engagement of the activating Fc receptor for monomeric IgA (FcαRI). In addition to monocytes, macrophages and eosinophils as FcαRI expressing immune cells, neutrophils are especially vigorous in eliminating IgA opsonized tumor cells. However, with IgG as single agent it appears almost impossible to activate neutrophils efficiently, as we have visualized by live cell imaging of tumor cell killing. In this study, we investigated Fc receptor expression, binding and signaling to clarify why triggering of neutrophils by IgA is more efficient than by IgG. FcαRI expression on neutrophils is ~2 times and ~20 times lower than that of Fcγ receptors FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIb, but still, binding of neutrophils to IgA- or IgG-coated surfaces was similar. In addition, our data suggest that IgA-mediated binding of neutrophils is more stable compared to IgG. IgA engagement of neutrophils elicited stronger Fc receptor signaling than IgG as indicated by measuring the p-ERK signaling molecule. We propose that the higher stoichiometry of IgA to the FcαR/FcRγ-chain complex, activating four ITAMs (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activating Motifs) compared to a single ITAM for FcγRIIa, combined with a possible decoy role of the highly expressed FcγRIIIb, explains why IgA is much better than IgG at triggering tumor cell killing by neutrophils. We anticipate that harnessing the vast population of neutrophils by the use of IgA monoclonal antibodies can be a valuable addition to the growing arsenal of antibody-based therapeutics for cancer treatment.
Keywords: ADCC; CD89; Fc alpha receptor I; IgA; cancer; immunotherapy; neutrophil; signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Overdijk MB, Verploegen S, Bleeker WK, Parren PWHI. Chapter 13 - Role of IgG Fc receptors in monoclonal antibody therapy of cancer. In: Antibody Fc, Linking Adaptive and Innate Immunity. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc. (2014). p. 239–55. 10.1016/B978-0-12-394802-1.00013-3 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

