Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Pro-metastatic Chemokines and Aggressiveness Characteristics in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31031757
- PMCID: PMC6473166
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00757
Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Pro-metastatic Chemokines and Aggressiveness Characteristics in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
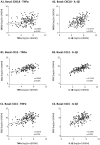
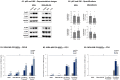
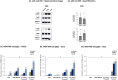
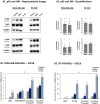
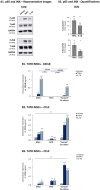
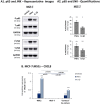
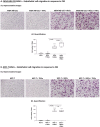
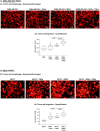
The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays key roles in promoting disease progression in the aggressive triple-negative subtype of breast cancer (TNBC; Basal/Basal-like). Here, we took an integrative approach and determined the impact of tumor-stroma-inflammation networks on pro-metastatic phenotypes in TNBC. With the TCGA dataset we found that the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β), as well as their target pro-metastatic chemokines CXCL8 (IL-8), CCL2 (MCP-1), and CCL5 (RANTES) were expressed at significantly higher levels in basal patients than luminal-A patients. Then, we found that TNFα- or IL-1β-stimulated co-cultures of TNBC cells (MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, BT-549) with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) expressed significantly higher levels of CXCL8 compared to non-stimulated co-cultures or each cell type alone, with or without cytokine stimulation. CXCL8 was also up-regulated in TNBC co-cultures with breast cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) derived from patients. CCL2 and CCL5 also reached the highest expression levels in TNFα/IL-1β-stimulated TNBC:MSC/CAF co-cultures. The elevations in CXCL8 and CCL2 expression partly depended on direct physical contacts between the tumor cells and the MSCs/CAFs, whereas CCL5 up-regulation was entirely dependent on cell-to-cell contacts. Supernatants of TNFα-stimulated TNBC:MSC "Contact" co-cultures induced robust endothelial cell migration and sprouting. TNBC cells co-cultured with MSCs and TNFα gained migration-related morphology and potent migratory properties; they also became more invasive when co-cultured with MSCs/CAFs in the presence of TNFα. Using siRNA to CXCL8, we found that CXCL8 was significantly involved in mediating the pro-metastatic activities gained by TNFα-stimulated TNBC:MSC "Contact" co-cultures: angiogenesis, migration-related morphology of the tumor cells, as well as cancer cell migration and invasion. Importantly, TNFα stimulation of TNBC:MSC "Contact" co-cultures in vitro has increased the aggressiveness of the tumor cells in vivo, leading to higher incidence of mice with lung metastases than non-stimulated TNBC:MSC co-cultures. Similar tumor-stromal-inflammation networks established in-culture with luminal-A cells demonstrated less effective or differently-active pro-metastatic functions than those of TNBC cells. Overall, our studies identify novel tumor-stroma-inflammation networks that may promote TNBC aggressiveness by increasing the pro-malignancy potential of the TME and of the tumor cells themselves, and reveal key roles for CXCL8 in mediating these metastasis-promoting activities.
Keywords: CCL2; CCL5; CXCL8; cancer-associated fibroblasts; interleukin 1β; mesenchymal stem cells; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor necrosis factor α.
Figures

References
-
- Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Bonotto M, Bolzonello S, Andreetta C, Moroso S, et al. Pattern of metastatic spread and prognosis of breast cancer biologic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:e12532 10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.e12532 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

