The Antidepressant Mirtazapine Inhibits Hepatic Innate Immune Networks to Attenuate Immune-Mediated Liver Injury in Mice
- PMID: 31031775
- PMCID: PMC6474187
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00803
The Antidepressant Mirtazapine Inhibits Hepatic Innate Immune Networks to Attenuate Immune-Mediated Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
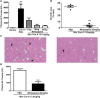
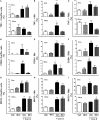
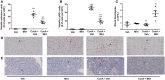
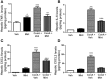
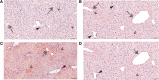
Activation of the innate immune system, including tissue macrophages and associated neutrophil infiltration, is an important driver of subsequent adaptive immune responses in many autoimmune diseases, including autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). The antidepressant mirtazapine has a unique complex pharmacology, altering signaling through a number of serotonin and histamine receptors that can impact macrophage function; an effect potentially influencing AIH outcome. In the mouse model of concanavalin A (Con A) induced liver injury (mimics many aspects of human AIH), in which early innate immune activation (i.e., stimulated hepatic macrophages/monocytes recruit neutrophils and additional monocytes to the liver) critically drives immune-mediated hepatitis induction, mirtazapine strikingly and dose-dependently inhibited Con A-induced liver injury. This inflammation-suppressing effect of mirtazapine was linked to an attenuation of Con A-stimulated early innate immune responses within the liver, including inhibition of hepatic macrophage/monocyte activation, decreased hepatic macrophage/monocyte-derived pro-inflammatory cytokine (e.g., TNFα) and chemokine (e.g., CXCL1 and CXCL2) production, suppression of Con A-induced increases in the hepatic expression of the neutrophil relevant endothelial cell adhesion molecule ICAM-1, with the resultant significant reduction in neutrophil recruitment into the liver. Consistent with our findings in the Con A model, mirtazapine also significantly reduced activation-induced release of cytokine/chemokine mediators from human CD14+ monocytes in vitro. Conclusion: Our data suggest that mirtazapine can attenuate hepatic innate immune responses that critically regulate the subsequent development of autoimmune liver injury. Therefore, given that it is a safe and widely used medication, mirtazapine may represent a novel therapeutic approach to autoimmune liver disease.
Keywords: autoimmunity; chemokine; cytokine; flow cytometry; inflammation; macrophage; neutrophil.
Figures
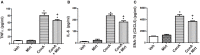

Similar articles
-
The Antidepressant Mirtazapine Activates Hepatic Macrophages, Facilitating Pathogen Clearance While Limiting Tissue Damage in Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 3;11:578654. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.578654. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33250892 Free PMC article.
-
The Antidepressant Mirtazapine Rapidly Shifts Hepatic B Cell Populations and Functional Cytokine Signatures in the Mouse.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 25;12:622537. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.622537. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33841403 Free PMC article.
-
Corilagin Ameliorates Con A-Induced Hepatic Injury by Restricting M1 Macrophage Polarization.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 13;12:807509. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.807509. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095894 Free PMC article.
-
More Than Suppression: Glucocorticoid Action on Monocytes and Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 27;10:2028. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02028. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31507614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
Cited by
-
Inverse Association between Serotonin 2A Receptor Antagonist Medication Use and Mortality in Severe COVID-19 Infection.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J. 2020 Sep 15;4(4):1-5. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J. 2020. PMID: 33117497 Free PMC article.
-
Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia is Associated with Increased Plasma Immunoglobulin G Agonist Autoantibodies Targeting the 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2A Receptor.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Feb 2;5(1):1-9. doi: 10.31038/EDMJ.2021511. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J. 2021. PMID: 33680365 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Regulatory and Molecular Effects of Antidepressants on the Inflamed Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cell Line.Neurotox Res. 2021 Aug;39(4):1211-1226. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00367-5. Epub 2021 May 4. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 33945102 Free PMC article.
-
Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Current Insights and Impact on Quality of Life.Hepat Med. 2021 Aug 28;13:83-92. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S256692. eCollection 2021. Hepat Med. 2021. PMID: 34483690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-arrestin2 deficiency ameliorates S-100-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice by inhibiting infiltration of monocyte-derived macrophage and attenuating hepatocyte apoptosis.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Oct;44(10):2048-2064. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01103-9. Epub 2023 May 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37225848 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

