Nanotechnology in metastatic cancer treatment: Current Achievements and Future Research Trends
- PMID: 31031845
- PMCID: PMC6485233
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.28394
Nanotechnology in metastatic cancer treatment: Current Achievements and Future Research Trends
Abstract
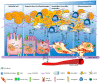
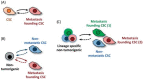
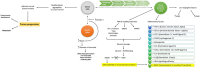
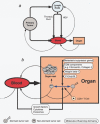
The systemic spread of malignant cells from a primary site, a process termed metastasis represents a global challenge in cancer treatment. There is a real need to develop novel therapy strategies and nanomedicine may have remarkable and valuable contribution through specific and selective delivery of chemotherapeutic agents, through its intrinsic cytotoxic activity or through imaging applications, appealing also in the context of cancer personalized therapy. This review is focused on the applications of nanoparticles in the treatment of metastatic cancer, particularly on the possible effect on cell stabilization, growth inhibition, eventual interaction with adhesion molecules and antiangiogenic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Development and evaluation of a CEACAM6-targeting theranostic nanomedicine for photoacoustic-based diagnosis and chemotherapy of metastatic cancer.Theranostics. 2018 Jul 30;8(15):4247-4261. doi: 10.7150/thno.25131. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30128051 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design of multimodal therapeutic nanosystems for effective inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis.Acta Biomater. 2018 Sep 1;77:240-254. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.07.025. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30012354
-
Engineered Hybrid Nanoparticles for On-Demand Diagnostics and Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Dec 15;48(12):3016-25. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00316. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 26605438
-
The emerging applications of magnetic nanovectors in nanomedicine.Pharm Pat Anal. 2015;4(4):285-304. doi: 10.4155/ppa.15.17. Pharm Pat Anal. 2015. PMID: 26174567 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-Free Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Enable Suppression of Cancer Metastasis and Confer Survival Advantages to Mice with Tumor Xenografts.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Nov 13;16(45):61787-61804. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c16609. Epub 2024 Oct 24. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39448366 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Responsive Nanocarriers in Cancer Treatment: A Review.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 Mar 3;4(2):589-612. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00212. eCollection 2021 Apr 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 33860189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhalable Formulations to Treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Recent Therapies and Developments.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 31;15(1):139. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010139. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary Delivery of Anticancer Drugs via Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Lung Cancer: An Update.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jul 27;14(8):725. doi: 10.3390/ph14080725. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Current Understanding of Hypoxia Mediated Tumour Progression for Nanotherapeutic Development.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 11;11(12):1989. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121989. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31835751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

