The Effects of Acupuncture on Hemodynamic Changes During Endotracheal Intubation for General Anesthesia
- PMID: 31031879
- PMCID: PMC6484345
- DOI: 10.1089/acu.2018.1330
The Effects of Acupuncture on Hemodynamic Changes During Endotracheal Intubation for General Anesthesia
Abstract
Objective: The goal of this research was to investigate the efficacy of perioperative manual acupuncture in the LV 3 and LI 4 points for lessening hemodynamic changes during endotracheal intubation in patients who were receiving anesthesia. Materials and Methods: This double-blinded randomized controlled study enrolled patients who were undergoing endotracheal intubation, in 2015-2016, during general anesthesia in the general surgery department of the Imam Khomeini Hospital complex, in the Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran. The patients were randomly allocated into 2 groups with 30 patients in each group. In the treatment group, acupuncture needles were placed at LV 3 and LI 4, whereas, in the control group, the needles were placed 1 cm lateral to these points. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), and heart rate (HR) before and after placing the acupuncture needles, after induction, immediately, 1 minute, and 3 minutes after intubation were measured and recorded prospectively. Results: The patients had a mean age of 44.45 ± 12.72 years and included 35 (58.3%) males. Before acupuncture, demographic data, mean blood pressure (BP), and mean HR of the patients were not significantly different in the treatment and control groups. The mean SBP, DBP, MAP, and HR of all patients changed over time significantly (P < 0.001 for all). In the treatment group, mean SBP, DBP, and MAP changes immediately after the needles were placed were significantly less than those in the control group (P = 0.033, 0.024, and 0.024, respectively). Conclusions: Although acupuncture could have a very-short-term effect that reduces BP during endotracheal intubation, hemodynamic changes might not be prevented during endotracheal intubation.
Keywords: acupuncture; hemodynamic indices; intubation.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial conflicts exist.
Figures
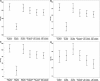
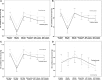
References
-
- Dix P, Howell S. Survey of cancellation rate of hypertensive patients undergoing anaesthesia and elective surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2001;86(6):789–793 - PubMed
-
- Kayhan Z, Aldemir D, Mutlu H, Ögüs E. Which is responsible for the haemodynamic response due to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation—catecholamines, vasopressin or angiotensin? Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005;22(10):780–785 - PubMed
-
- Russell WJ, Morris RG, Frewin DB, Drew SE. Changes in plasma catecholamine concentrations during endotracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1981;53(8):837–839 - PubMed
-
- Mendonca FT, de Queiroz LM, Guimaraes CC, Xavier AC. Effects of lidocaine and magnesium sulfate in attenuating hemodynamic response to tracheal intubation: Single-center, prospective, double-blind, randomized study. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2017;67(1):50–56 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
