Effects of Donepezil Hydrochloride on Neuronal Response of Pyramidal Neurons of the CA1 Hippocampus in Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31031898
- PMCID: PMC6484192
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.9.10.305
Effects of Donepezil Hydrochloride on Neuronal Response of Pyramidal Neurons of the CA1 Hippocampus in Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Donepezil (DON), an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor (AChEI), is widely used in the treatment of Alzheimer's Disease (AD). The current study aimed at evaluating the effect of donepezil hydrochloride on pyramidal neuron response in CA1 region of a rat model of AD.
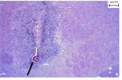
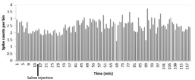
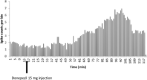
Methods: In the current experimental study, adult male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups: Nucleus Basalis Magnocellularis (NBM) lesion (the lesions were induced by an electrical method of 0.5 m A, for 3 s in NBM) and three donepezil groups (lesions plus 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg donepezil intraperitoneal injection). Neuronal spontaneous activity to injection of the donepezil and saline were recorded in CA1 region of hippocampal.
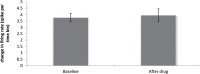
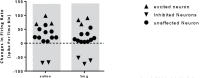
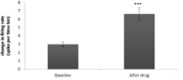
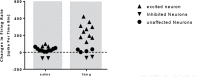
Results: The obtained results showed that IntraPeritoneal (IP) injection of donepezil (10 and 15 mg/kg) increased neuronal spontaneous activity in the rat model of AD.
Conclusion: The current study results suggested that acute IP injection of donepezil increased neuronal response in CA1 region of hippocampal in a rat model of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease; Donepezil; Electrophysiology; Rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Arias E., Gallego-Sandin S., Villarroya M., Garcia A. C., Lopez M. G. (2005). Unequal neuroprotection afforded by the acetylcholineestrase inhibitors galantamine, donepezil and rivastigmine in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: Role of nicotinic receptors. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 315(3), 1349–53. [DOI:10.1124/jpet.105.090365] - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
