Understanding the financial cost of robotic lobectomy: calculating the value of innovation?
- PMID: 31032202
- PMCID: PMC6462550
- DOI: 10.21037/acs.2018.05.18
Understanding the financial cost of robotic lobectomy: calculating the value of innovation?
Abstract
Background: The advantages of a minimally-invasive surgical approach compared to conventional open thoracotomy for lung resection have been previously described. While robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS) has shown comparable clinical outcomes for lobectomy as compared with video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS), the cost and inherent value associated with the robotic technology remains a main concern.
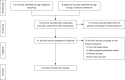
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of the literature on the cost of RATS lobectomy using studies published prior to December 2017 on MEDLINE and EMBASE.
Results: Six observational studies met our inclusion criteria. Median cost of RATS lobectomy ranged from $15,440 to $22,582. Operating room (OR) cost was a major contributing factor to overall cost. The lowest per-procedure cost was reported by the highest volume center. Cost definitions were highly variable among studies. The total cost of RATS was similar or lower to open lobectomy, and higher than that of VATS, with cost difference ranging from $2,901 to $4,708.
Conclusions: Assessment of cost for RATS lobectomy varies significantly. High OR costs may be offset by improved outcomes as compared with open lobectomy, but currently the costs exceed that of VATS lobectomy. Further work is needed to define the cost and actual value parameters for RATS lobectomy.
Keywords: Robotic surgery; cost; cost-effectiveness; lobectomy; minimally-invasive.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Park BJ, Heerdt PM. Minimally invasive surgical techniques in the treatment of lung cancer. Minerva Chir 2009;64:573-88. - PubMed
-
- Falcoz PE, Puyraveau M, Thomas PA, et al. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery versus open lobectomy for primary non-small-cell lung cancer: a propensity-matched analysis of outcome from the European Society of Thoracic Surgeon database. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2016;49:602-9. 10.1093/ejcts/ezv154 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous