Clinical Efficacy of CyberKnife Radiosurgery for Adult Brainstem Glioma: 10 Years Experience at Tianjin CyberKnife Center and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 31032223
- PMCID: PMC6473059
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00257
Clinical Efficacy of CyberKnife Radiosurgery for Adult Brainstem Glioma: 10 Years Experience at Tianjin CyberKnife Center and Review of the Literature
Abstract
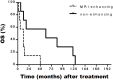
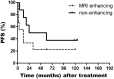
Background: Brainstem glioma is a rare brain tumor with poor prognosis and difficulty for surgical resection. We sought to retrospectively analyze and evaluate the clinical efficacy of CyberKnife for brainstem gliomas. Methods: From 2006 to 2015, a total of 21 brainstem gliomas patients who received CyberKnife radiosurgery treatment enrolled in this study and 18 patients with follow up. CyberKnife image-guided radiosurgical system were applied consecutively with the median prescribed total dose of 26 Gy (14-33 Gy) at two to six fractions on days utilizing CyberKnife system, and the median biological equivalent doses of 59.8 Gy (33.6-76.56 Gy). The clinic pathlogical features, survival were analyzed to explore the efficacy of CyberKnife radiosurgery in treatment of brainstem glioma. Results: With median follow-up of 54.5 months, patients with brainstem gliomas had median overall survival of 19 months, five patients still alive. The primary endpoints of the 1- and 2-year overall survival rates were 87.5 and 52.4%, respectively. During the treatment course, six patients were observed to have pseudoprogression with mass effect on MRI. Four patients developed radiation complications. Grade 2 radiation-related toxicity were observed in three patients and one patient with grade 3. Conclusion: The efficacy of brainstem gliomas-treated with CyberKnife is efficacious with mild toxicity.
Keywords: CyberKnife; brainstem gliomas; prognostic factor; radiosurgery; stereotactic body radiotherapy.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

