Xuebijing injection for acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31032267
- PMCID: PMC6465435
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2018.12.22
Xuebijing injection for acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Xuebijing injection (XBJ) treatment for acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning.
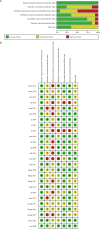
Methods: Using the PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, Sinomed, Wanfang, CNKI, and Weipu (VIP) databases from the beginning of the datasets until December 2017, all of the relevant randomized controlled trials were identified. Relative risks (RR), weighted mean difference (WMD), along with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were used to analyze the main outcomes. Statistical analysis was performed using the RevMan software version 5.3. The qualities of the involved studies were assessed by the risk of bias according to the Cochrane handbook.
Results: Twenty-six randomized controlled trials with 1,880 participants were collected in total. Compared with just conventional therapy alone, XBJ combined with conventional therapy significantly reduced the 7-day mortality rate (RR: 0.33; 95% CI: 0.22-0.49), CRP in the 50 mL group (WMD: -11.60; 95% CI: -14.38 to -8.83), CRP in the 100 mL group (WMD: -1.73; 95% CI: -2.91 to -0.55), AChE in the 50 mL group (WMD: -4.58;95% CI: -5.87 to -3.28), AChE in the 100 mL group (WMD: -1.73; 95% CI: -2.07 to -1.39), hospital stays in the 50 mL group (WMD: -4.26; 95% CI: -4.89 to -3.64), TNF-α in the 50 mL group (WMD: -2.66; 95% CI: -4.99 to -0.32), NF-κB in the 50 mL group (WMD: -13.07; 95% CI: -14.67 to -11.47), and CK-MB in the 50 mL group (WMD: -32.28; 95% CI: -40.62 to -23.93). However, there was no statistical difference of TNF-α in the 100 mL group (WMD: -2.17; 95% CI: -4.66 to 0.32).
Conclusions: XBJ has a significant clinical efficacy for the treatment of patients with acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. The most effective dose is 50 mL, while the most effective frequency is twice a day. However, more studies are needed to confirm the extract efficacy of XBJ.
Keywords: Xuebijing injection (XBJ); acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning (AOPP); meta-analysis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Xuebijing in the treatment of patients with sepsis.Am J Emerg Med. 2017 Feb;35(2):285-291. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Am J Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 27852528
-
[Xuebijing improves clinical prognosis and reduces mortality in patients with acute paraquat poisoning: a Meta-analysis included 1 429 patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Nov;31(11):1416-1422. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.11.020. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31898576 Chinese.
-
Efficacy of Xuebijing Injection for Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 26;2021:6621368. doi: 10.1155/2021/6621368. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34221082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Clinical efficacy and safety of Xuebijing injection on sepsis: a Meta-analysis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jun;32(6):691-695. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200427-00475. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32684214 Chinese.
-
Hemoperfusion in combination with hemofiltration for acute severe organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Res Med Sci. 2022 Apr 15;27:33. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_822_20. eCollection 2022. J Res Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35548179 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early enteral nutrition combined with PSS-based nursing in the treatment of organophosphorus pesticide poisoning.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):9315-9323. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34540048 Free PMC article.
-
Xiao'er Xiaoji Zhike Oral Liquid Combined with Azithromycin for Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jul 19;2020:9740841. doi: 10.1155/2020/9740841. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32765636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Z, Lv Y, Cui T. Analysis of cause of death by acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Zhong Guo She Qu Yi Shi 2012;14:106-7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
