Single-Center Analysis of Human Papillomavirus Infection and P16INK4A Expression among Korean Patients with Penile Cancer
- PMID: 31032357
- PMCID: PMC6457309
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/6940582
Single-Center Analysis of Human Papillomavirus Infection and P16INK4A Expression among Korean Patients with Penile Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the statuses of P16INK4A expression and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection among patients with penile cancer at a single Korean institution.
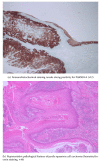
Patients and methods: Fourteen patients with penile cancer at our center were retrospectively identified and their clinicopathological data were analyzed. The patients' HPV and P16INK4A expression status (a known tumor suppressor protein) were tested using genotyping with a DNA chip assay and immunohistochemical staining, respectively. The results regarding HPV status were compared to those from another Asian study.
Results: The mean age at diagnosis was 60 years (range: 34-86 years). The median tumor size was 3.0 cm (range: 0.6-4.7 cm). Ten tumors were located on the penile glans. Five patients tested positive for HPV DNA (5/14, 36%) and all cases involved HPV type 16 (5/5, 100%). Positive expression of P16INK4A was observed in 6 cases (6/14, 43%). Among the HPV positive cases, 80% of cases (4/5) were also positive for P16INK4A. The prevalence of HPV infection in our study (36%) was higher than in a previous Asian study (23%).
Conclusions: This is the first study to evaluate the prevalence of HPV infection and P16INK4A expression among patients with penile cancer at a single Korean institution. The prevalence of HPV (36%) was slightly higher than the results from a previous Asian study. Additional multi-center studies are needed to better understand penile cancer in Korea and to identify biomarkers that can determine high-risk cases and predict their prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P16INK4a expression in patients with penile cancer.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 12;13(10):e0205350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205350. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30312320 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of HPV with overexpression of p16INK4a protein and EBV infection in penile cancer-A series of cases from Brazil Amazon.PLoS One. 2020 May 6;15(5):e0232474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232474. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32374757 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus genotypes and P16INK4A expression in squamous penile carcinoma in Mexican patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Dec 19;19(1):1068. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4696-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31856740 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of human papillomavirus DNA and p16INK4a in penile cancer and penile intraepithelial neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20(1):145-158. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30682-X. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30573285
-
The Prognostic Role of HPV or p16INK4a Status in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2025 Jan 3;23(2):e247078. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2024.7078. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2025. PMID: 39752880
Cited by
-
The relationship of human papillomavirus positivity with tumor characteristics in an Irish penile cancer population.Can Urol Assoc J. 2022 Dec;16(12):435-438. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.7821. Can Urol Assoc J. 2022. PMID: 36656691 Free PMC article.
-
Preventable Cancers Caused by Infection in Korea From 2015 to 2030.J Korean Med Sci. 2025 Jul 7;40(26):e143. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e143. J Korean Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40625045 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic literature review on the clinical and economic burden of human papillomavirus-related diseases in select areas in the Asia-Pacific region.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2425535. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2425535. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39552456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hakenberg O. W., Comperat E. M., Minhas S., Necchi A., Protzel C., Watkin N. EAU guidelines on penile cancer. European Urology. 2015;67:142–150. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous