RUNX represses Pmp22 to drive neurofibromagenesis
- PMID: 31032403
- PMCID: PMC6482019
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau8389
RUNX represses Pmp22 to drive neurofibromagenesis
Abstract
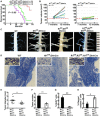
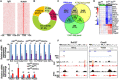
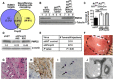
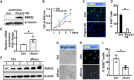
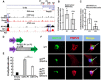
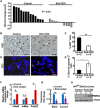
Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) are predisposed to develop neurofibromas, but the underlying molecular mechanisms of neurofibromagenesis are not fully understood. We showed dual genetic deletion of Runx1 and Runx3 in Schwann cells (SCs) and SC precursors delayed neurofibromagenesis and prolonged mouse survival. We identified peripheral myelin protein 22 (Pmp22/Gas3) related to neurofibroma initiation. Knockdown of Pmp22 with short hairpin RNAs increased Runx1fl/fl;Runx3fl/fl;Nf1fl/fl;DhhCre tumor-derived sphere numbers and enabled significantly more neurofibroma-like microlesions on transplantation. Conversely, overexpression of Pmp22 in mouse neurofibroma SCs decreased cell proliferation. Mechanistically, RUNX1/3 regulated alternative promoter usage and induced levels of protein expression of Pmp22 to control SC growth. Last, pharmacological inhibition of RUNX/core-binding factor β (CBFB) activity significantly reduced neurofibroma volume in vivo. Thus, we identified a signaling pathway involving RUNX1/3 suppression of Pmp22 in neurofibroma initiation and/or maintenance. Targeting disruption of RUNX/CBFB interaction might provide a novel therapy for patients with neurofibroma.
Figures
References
-
- Dombi E., Baldwin A., Marcus L. J., Fisher M. J., Weiss B., Kim A., Whitcomb P., Martin S., Aschbacher-Smith L. E., Rizvi T. A., Wu J., Ershler R., Wolters P., Therrien J., Glod J., Belasco J. B., Schorry E., Brofferio A., Starosta A. J., Gillespie A., Doyle A. L., Ratner N., Widemann B. C., Activity of selumetinib in neurofibromatosis type 1-related plexiform neurofibromas. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 2550–2560 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jessen W. J., Miller S. J., Jousma E., Wu J., Rizvi T. A., Brundage M. E., Eaves D., Widemann B., Kim M.-O., Dombi E., Sabo J., Hardiman Dudley A., Niwa-Kawakita M., Page G. P., Giovannini M., Aronow B. J., Cripe T. P., Ratner N., MEK inhibition exhibits efficacy in human and mouse neurofibromatosis tumors. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 340–347 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pemov A., Li H., Patidar R., Hansen N. F., Sindiri S., Hartley S. W., Wei J. S., Elkahloun A., Chandrasekharappa S. C.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program, Boland J. F., Bass S.; NCI DCEG Cancer Genomics Research Laboratory, Mullikin J. C., Khan J., Widemann B. C., Wallace M. R., Stewart D. R., The primacy of NF1 loss as the driver of tumorigenesis in neurofibromatosis type 1-associated plexiform neurofibromas. Oncogene 36, 3168–3177 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

