TGF-β2 is an exercise-induced adipokine that regulates glucose and fatty acid metabolism
- PMID: 31032475
- PMCID: PMC6481955
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-018-0030-7
TGF-β2 is an exercise-induced adipokine that regulates glucose and fatty acid metabolism
Abstract
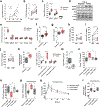
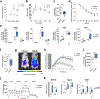
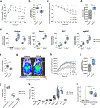
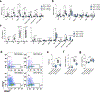
Exercise improves health and well-being across diverse organ systems, and elucidating mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of exercise can lead to new therapies. Here, we show that transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2) is secreted from adipose tissue in response to exercise and improves glucose tolerance in mice. We identify TGF-β2 as an exercise-induced adipokine in a gene expression analysis of human subcutaneous adipose tissue biopsies after exercise training. In mice, exercise training increases TGF-β2 in scWAT, serum, and its secretion from fat explants. Transplanting scWAT from exercise-trained wild type mice, but not from adipose tissue-specific Tgfb2-/- mice, into sedentary mice improves glucose tolerance. TGF-β2 treatment reverses the detrimental metabolic effects of high fat feeding in mice. Lactate, a metabolite released from muscle during exercise, stimulates TGF-β2 expression in human adipocytes. Administration of the lactate-lowering agent dichloroacetate during exercise training in mice decreases circulating TGF-β2 levels and reduces exercise-stimulated improvements in glucose tolerance. Thus, exercise training improves systemic metabolism through inter-organ communication with fat via a lactate-TGF-β2-signaling cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


Comment in
-
A new metabolic role for TGFβ2.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Apr;15(4):191. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0183-9. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30787450 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fiuza-Luces C, Garatachea N, Berger NA & Lucia A Exercise is the Real Polypill. Physiology 28, 330–358 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK102898/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101043/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099511/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126705/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK114550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK082659/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK112283/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007260/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077097/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138738/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK111714/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK102320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145064/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

