Human Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Neutralizes Adverse Effects of Gulf War Illness (GWI) Serum in Neural Cultures: Paving the Way to Immunotherapy for GWI
- PMID: 31032477
- PMCID: PMC6486180
- DOI: 10.29245/2572.942X/2018/5.1219
Human Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Neutralizes Adverse Effects of Gulf War Illness (GWI) Serum in Neural Cultures: Paving the Way to Immunotherapy for GWI
Abstract
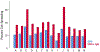
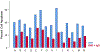
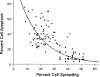
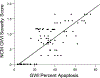
Gulf War Illness (GWI) is a chronic debilitating disease of unknown etiology that affects the brain and has afflicted many veterans of the 1990-91 Gulf War (GW). We showed recently1 that blood serum from patients suffering from GWI exerts detrimental effects on neural cultures, including reduced growth, increased apoptosis, and disruption of neural network function. Remarkably, these adverse effects were prevented by the concomitant addition to the culture of serum from healthy Gulf War (GW) era veterans. We interpreted those findings1 in the context of our hypothesis that GWI is, at least partly, due to circulating pathogenic persistent antigens2, probably coming from vaccines administered to GW veterans who lacked crucial Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) class 2 alleles3 and, therefore, could not make antibodies against those antigens; by contrast, healthy GW veterans who received the same vaccines and possessed HLA protection3 made antibodies that neutralized the various antigens. Thus, we hypothesized that the beneficial effect of the healthy serum on preventing the adverse GWI serum effects was due to the presence of antibodies against the persistent antigens. Here we tested this hypothesis by assessing the effect of pooled human immunoglobulin G (IgG) on ameliorating the GWI adverse effects on neural growth and apoptosis in neuroblastoma N2A cultures. We tested this effect in 14 GWI patients and found that IgG exerted a potent ameliorating effect by inhibiting the reduction in growth and increased apoptosis of GWI serum. These results lend support to our persistent antigen hypothesis1,2 and suggest an immunotherapy approach for treating GWI. This approach is further strengthened by our finding that the severity of GWI neurocognitive/mood (NCM) symptoms was positively correlated with the degree of apoptosis caused by GWI serum on the neural culture, thus validating the relevance of the apoptotic effect to NCM symptomatology. Finally, we used this relation to predict NCM scores based on the reduced apoptosis effected by IgG addition and found a predicted reduction in NCM symptom severity by ~60%. Altogether, these findings point to the possible beneficial use of IgG in treating GWI.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Blood serum; Gulf War Illness; IgG; Neural cultures; Neural growth.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vaccine-Induced Adverse Effects in Cultured Neuroblastoma 2A (N2A) Cells Duplicate Toxicity of Serum from Patients with Gulf War Illness (GWI) and Are Prevented in the Presence of Specific Anti-Vaccine Antibodies.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 May 18;8(2):232. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020232. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32443454 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax and Gulf War Illness (GWI): Evidence for the Presence of Harmful Anthrax Antigen PA63 In the Serum of Veterans with GWI.J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2019 Nov 25;4(6):1-9. doi: 10.29245/2572.942x/2019/6.1255. J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2019. PMID: 40747435 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse effects of Gulf War Illness (GWI) serum on neural cultures and their prevention by healthy serum.J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2018;3(2):19-27. doi: 10.29245/2572.942X/2018/2.1177. Epub 2018 Apr 27. J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2018. PMID: 31032476 Free PMC article.
-
A review of pre-clinical models for Gulf War Illness.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Dec;228:107936. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107936. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34171340 Review.
-
Calcium Hypothesis of Gulf War Illness: Role of Calcium Ions in Neurological Morbidities in a DFP-Based Rat Model for Gulf War Illness.Neurosci Insights. 2020 Dec 10;15:2633105520979841. doi: 10.1177/2633105520979841. eCollection 2020. Neurosci Insights. 2020. PMID: 33354668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vaccine-Induced Adverse Effects in Cultured Neuroblastoma 2A (N2A) Cells Duplicate Toxicity of Serum from Patients with Gulf War Illness (GWI) and Are Prevented in the Presence of Specific Anti-Vaccine Antibodies.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 May 18;8(2):232. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020232. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32443454 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax and Gulf War Illness (GWI): Evidence for the Presence of Harmful Anthrax Antigen PA63 In the Serum of Veterans with GWI.J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2019 Nov 25;4(6):1-9. doi: 10.29245/2572.942x/2019/6.1255. J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2019. PMID: 40747435 Free PMC article.
-
In silico Analysis of the Binding Affinities of Antigenic Epitopes of Vaccines Administered to Gulf War Veterans to Specific HLA Class II Alleles Protective for Gulf War Illness.J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2019 Oct 19;4(5):23-30. doi: 10.29245/2572.942x/2019/5.1254. J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2019. PMID: 40746427 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Stem Cells from Toxicity Induced by Gulf War Illness (GWI) Serum in N2A Neuroblastoma Cells.J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2021 Aug 20;6(1):26-31. doi: 10.29245/2572.942x/2021/1.1281. J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2021. PMID: 40370960 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Antigens Hypothesis: The Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Connection.J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2018 Dec 24;3(6):27-1. doi: 10.29245/2572.942x/2018/6.1235. J Neurol Neuromedicine. 2018. PMID: 40370508 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fukuda K, Nisenbaum R, Stewart G, et al. Chronic multisymptom illness affecting Air Force veterans of the Gulf War. JAMA. 1998; 280: 981–8. - PubMed
-
- Kang HK, Li B, Mahan CM, et al. Health of US veterans of 1991 Gulf War: a follow-up survey in 10 years. J Occup Environ Med. 2009; 51: 401–10. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
