AMPK activation induced in pemetrexed-treated cells is associated with development of drug resistance independently of target enzyme expression
- PMID: 31033201
- PMCID: PMC6547620
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12496
AMPK activation induced in pemetrexed-treated cells is associated with development of drug resistance independently of target enzyme expression
Abstract
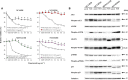
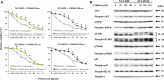
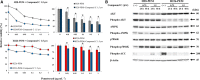
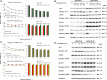
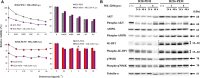
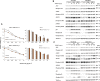
Pemetrexed (PEM) inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis and is currently one of the first-line agents for mesothelioma. PEM suppresses the activities of several enzymes involved in purine and pyrimidine synthesis, and elevated activity of these enzymes in tumors is often linked with resistance to PEM. The agent also stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and consequently influences the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathways. Nevertheless, it remains unclear whether PEM resistance is linked to the AMPK or mTORC1 pathways. Here, we established two independent PEM-resistant mesothelioma cell lines in which expression of the PEM-target enzymes was not elevated, and found that levels of phosphorylated AMPK and p70S6K and, to a lesser extent, levels of phosphorylated AKT and p53, were increased in these cells as compared with the respective parent cells. PEM stimulation also augmented phosphorylation of AMPK, p70S6K, AKT and p53 in most cases. An AMPK activator increased phosphorylation and PEM resistance in parental cells, and the inhibitor decreased the resistance of PEM-resistant cells. In contrast, inhibitors for p70S6K and AKT did not influence PEM resistance; furthermore, increased levels of endogenous p53 did not affect PEM sensitivity. These data collectively indicate that constitutive activation of AMPK is associated with PEM resistance, and that this is unconnected with elevated DNA and RNA synthesis.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; drug resistance; mTORC1; mesothelioma; pemetrexed.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests in this research. We obtained a grant from Nichias Corporation. Nichias Corporation is not a pharmaceutical company but a company making industrial products for building, automobiles and pipes (see
Figures

References
-
- Borgdorff V, Rix U, Winter GE, Gridling M, Müller AC, Breitwieser FP, Wagner C, Colinge J, Bennett KL, Superti‐Furga G et al (2014) A chemical biology approach identifies AMPK as a modulator of melanoma oncogene MITF. Oncogene 33, 2531–2539. - PubMed
-
- Bronte G, Incorvaia L, Rizzo S, Passiglia F, Galvano A, Rizzo F, Rolfo C, Fanale D, Listì A, Natoli C et al (2016) The resistance related to targeted therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: why has not the target been hit yet? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 107, 20–32. - PubMed
-
- Di Marzo D, Forte IM, Indovina P, Di Gennaro E, Rizzo V, Giorgi F, Mattioli E, Iannuzzi CA, Budillon A, Giordano A et al (2014) Pharmacological targeting of p53 through RITA is an effective antitumoral strategy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cell Cycle 13, 652–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

