Eccentric and Concentric Resistance Exercise Comparison for Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 31033900
- PMCID: PMC6746593
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002010
Eccentric and Concentric Resistance Exercise Comparison for Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to compare the efficacy of eccentrically focused resistance exercise (ECC RT) to concentrically focused resistance exercise (CNC RT) on knee osteoarthritis (OA) symptoms and strength.
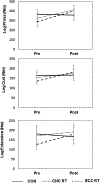
Methods: Ninety participants consented. Participants were randomized to CNC RT, ECC RT, or a wait-list, no-exercise control group. Four months of supervised exercise training was completed using traditional weight machines (CNC RT) or modified-matched machines that overloaded the eccentric action (ECC RT). Main outcomes included one-repetition maximal strength (knee extension, leg flexion, and leg press), weekly rate of strength gain, Western Ontario and McMaster University Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) total score and subscores.
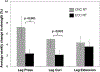
Results: Fifty-four participants (60-85 yr, 61% women) completed the study. Both CNC RT and ECC RT groups showed 16%-28% improvement relative to the wait-list, no-exercise control group (P = 0.003-0.005) for all leg strength measures. The rate of weekly strength gain was greater for CNC RT than for ECC RT for leg press and knee flexion (by 2.9%-4.8%; both, P < 0.05) but not knee extension (0.7%; P = 0.38). There were no significant differences in WOMAC total and subscores across groups over time. Leg press strength change was the greatest contributor to change in WOMAC total scores (R = 0.223). The change in knee flexion strength from baseline to month 4 was a significant predictor of the change in WOMAC pain subscore (F ratio = 4.84, df = 45, P = 0.032). Both modes of strength training were well tolerated.
Conclusions: Both resistance training types effectively increased leg strength. Knee flexion and knee extension muscle strength can modify function and pain symptoms irrespective of muscle contraction type. Which mode to pick could be determined by preference, goals, tolerance to the contraction type, and equipment availability.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Benefits of Resistance Training with Blood Flow Restriction in Knee Osteoarthritis.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018 May;50(5):897-905. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001530. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018. PMID: 29266093 Clinical Trial.
-
Strength Training for Arthritis Trial (START): design and rationale.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013 Jul 15;14:208. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-208. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013. PMID: 23855596 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Concentric and Eccentric Resistance Training Comparison on Physical Function and Functional Pain Outcomes in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 Oct;99(10):932-940. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001450. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 32324615 Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Resistance Training Dosing on Pain and Physical Function in Individuals With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Sports Health. 2020 Mar/Apr;12(2):200-206. doi: 10.1177/1941738119887183. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Sports Health. 2020. PMID: 31850826 Free PMC article.
-
Does blood flow restriction training enhance clinical outcomes in knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phys Ther Sport. 2021 May;49:37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2021.01.014. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Phys Ther Sport. 2021. PMID: 33582442
Cited by
-
Comparative Study Between the Mini-Open (≤2.5 Cm) Approach and Conventional Open Lateral Approach in the Surgical Treatment of Radial Head Fractures.J Pain Res. 2022 Oct 26;15:3413-3422. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S374599. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36320225 Free PMC article.
-
Reporting of Adverse Events in Randomized Controlled Trials of Therapeutic Exercise for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Phys Ther. 2021 Nov 1;101(11):pzab195. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab195. Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 34730830 Free PMC article.
-
Reporting of Harm in Randomized Controlled Trials of Therapeutic Exercise for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Phys Ther. 2021 Oct 1;101(10):pzab161. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab161. Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 34180534 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of exercise contributing to tissue regeneration.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Nov 30;7(1):383. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01233-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36446784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Effect of Catgut Embedding plus Warm Needle Moxibustion on Improving Inflammation and Quality of Life of Knee Osteoarthritis Patients.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 5;2022:5315619. doi: 10.1155/2022/5315619. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9856716. doi: 10.1155/2023/9856716. PMID: 36245835 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Munukka M, Waller B, Rantalainen T, et al. Efficacy of progressive aquatic resistance training for tibiofemoral cartilage in postmenopausal women with mild knee osteoarthritis: a randomised controlled trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(10):1708–17. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves RS, Pinheiro JP, Cabri J. Evaluation of potentially modifiable physical factors as predictors of health status in knee osteoarthritis patients referred for physical therapy. The Knee. 2012;19(4):373–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

