miRNAs, target genes expression and morphological analysis on the heart in gestational protein-restricted offspring
- PMID: 31034522
- PMCID: PMC6507319
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210454
miRNAs, target genes expression and morphological analysis on the heart in gestational protein-restricted offspring
Abstract
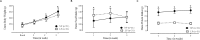
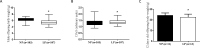
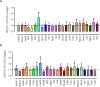
Gestational protein restriction was associated with low birth weight, hypertension and higher prevalence of cardiac disorders in adults. Several mechanisms, including epigenetics, could be related with the cardiovascular phenotype on protein-restricted offspring. Thus, we investigated the morphological cardiac effects of gestational protein restriction and left ventricle miRNAs and target genes expression pattern in both 12-day and 16-week old gestational protein-restricted male offspring. Pregnant Wistar rats were allocated into two groups, according to protein supply during pregnancy: NP (normal protein diet- 17%) or LP (low protein diet-6%). Dams on the gestational protein-restricted diet had lower body weight gain and higher food intake. Gestational protein-restricted offspring had low birth weight, followed by rapidly body weight recovery, hypertension, and increased myocytes cross-sectional area and collagen fraction at 16-week old age. At 12-days old, miR-184, miR-192, miR-376c, miR-380-3p, miR-380-5p, miR-451, and miR-582-3p had increased expression, and miR-547 and miR-743a had decreased expression in the gestational protein-restricted left ventricle. At 16-week old, let-7b, miR-125a-3p, miR-142-3p, miR-182 and miR-188-5p had increased expression and let-7g, miR-107, miR-127, miR-181a, miR-181c, miR-184, miR-324-5p, miR-383, miR-423-5p and miR-484 had decreased expression in gestational protein-restricted left ventricle. Target predicted gene expression analysis showed higher expression of Dnmt3a, Oxct1, Rictor and Trps1 and lower expression of Bbs1 and Calml3 in 12-day old protein-restricted offspring. 16-week old protein-restricted offspring had higher expression of Adrbk1, Bbs1, Dnmt3a, Gpr22, Inppl1, and Oxct1 genes. In conclusion, gestational protein restriction was related to offspring low birth weight, increased systolic blood pressure and morphological heart alterations that could be related to early heart miRNA expression changes that perpetuate into adulthood and which are associated with the regulation of essential genes involved in cardiovascular development, heart morphology, function, and metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

