The mitochondrial metabolic function of DJ-1 is modulated by 14-3-3β
- PMID: 31034784
- PMCID: PMC6988861
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201802754R
The mitochondrial metabolic function of DJ-1 is modulated by 14-3-3β
Abstract
Mitochondrial metabolic plasticity is a key adaptive mechanism in response to changes in cellular metabolic demand. Changes in mitochondrial metabolic efficiency have been linked to pathophysiological conditions, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and obesity. The ubiquitously expressed DJ-1 (Parkinsonism-associated deglycase) is known as a Parkinson's disease gene and an oncogene. The pleiotropic functions of DJ-1 include reactive oxygen species scavenging, RNA binding, chaperone activity, endocytosis, and modulation of major signaling pathways involved in cell survival and metabolism. Nevertheless, how these functions are linked to the role of DJ-1 in mitochondrial plasticity is not fully understood. In this study, we describe an interaction between DJ-1 and 14-3-3β that regulates the localization of DJ-1, in a hypoxia-dependent manner, either to the cytosol or to mitochondria. This interaction acts as a modulator of mitochondrial metabolic efficiency and a switch between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. Modulation of this novel molecular mechanism of mitochondrial metabolic efficiency is potentially involved in the neuroprotective function of DJ-1 as well as its role in proliferation of cancer cells.-Weinert, M., Millet, A., Jonas, E. A., Alavian, K. N. The mitochondrial metabolic function of DJ-1 is modulated by 14-3-3β.
Keywords: metabolic plasticity; mitochondrial efficiency; neuroprotective oncogenes.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by the Imperial College London funds provided to K.N.A. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

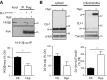
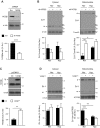
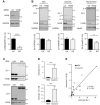
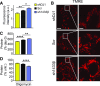
References
-
- Deng H., Wang P., Jankovic J. (2018) The genetics of Parkinson disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 42, 72–85 - PubMed
-
- Zhang L., Shimoji M., Thomas B., Moore D. J., Yu S. W., Marupudi N. I., Torp R., Torgner I. A., Ottersen O. P., Dawson T. M., Dawson V. L. (2005) Mitochondrial localization of the Parkinson’s disease related protein DJ-1: implications for pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 2063–2073 - PubMed
-
- Bonifati V., Rizzu P., Squitieri F., Krieger E., Vanacore N., van Swieten J. C., Brice A., van Duijn C. M., Oostra B., Meco G., Heutink P. (2003) DJ-1(PARK7), a novel gene for autosomal recessive, early onset parkinsonism. Neurol. Sci. 24, 159–160 - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T., Ishimori C., Takahashi-Niki K., Taira T., Kim Y. C., Maita H., Maita C., Ariga H., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. (2009) DJ-1 binds to mitochondrial complex I and maintains its activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 390, 667–672 - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa S., Taira T., Niki T., Takahashi-Niki K., Maita C., Maita H., Ariga H., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. (2009) Oxidative status of DJ-1-dependent activation of dopamine synthesis through interaction of tyrosine hydroxylase and 4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (L-DOPA) decarboxylase with DJ-1. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 28832–28844 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

