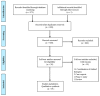
The Effect of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) in the Treatment of Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 31035414
- PMCID: PMC6566697
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11050977
The Effect of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) in the Treatment of Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Many cancer patients on intensive chemotherapy lack vitamin C. Vitamin C stimulates the production and activation of immune cells, so perhaps supplementation could be used to improve the immunity in those patients. This review assesses the effectiveness and safety of vitamin C administration in cancer. The PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched and all study designs except for phase I studies, and case reports were included in this review. A total of 19 trials were included. In only 4 trials randomization was used to determine if patients received vitamin C or a placebo. The result of this review does not prove that there is a clinically relevant positive effect of vitamin C supplementation in cancer patients in general on the overall survival, clinical status, quality of life (QOL) and performance status (PS), since the quality of the studies published is low. Interventions and patient groups are very diverse, hence an effect in some patient groups is possible. There seems to be a better effect with intravenous than oral administration. Nevertheless, treatment with vitamin C is safe with minimal side effects. Thereby, we think it is safe to examine the effects of vitamin C on specific groups of patients in a randomized controlled setting.
Keywords: adverse events; ascorbic acid; cancer; overall survival; supplementation; vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Q., Espey M.G., Sun A.Y., Pooput C., Kirk K.L., Krishna M.C., Khosh D.B., Drisko J., Levine M. Pharmacologic doses of ascorbate act as a prooxidant and decrease growth of aggressive tumor xenografts in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:11105–11109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804226105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical