Fast Tac Metabolizers at Risk ⁻ It is Time for a C/D Ratio Calculation
- PMID: 31035422
- PMCID: PMC6572069
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8050587
Fast Tac Metabolizers at Risk ⁻ It is Time for a C/D Ratio Calculation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Fast Tac Metabolizers at Risk-It is Time for a C/D Ratio Calculation. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 587.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 4;8(11):1870. doi: 10.3390/jcm8111870. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31690025 Free PMC article.
Abstract
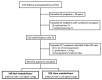
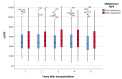
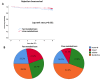
Tacrolimus (Tac) is a part of the standard immunosuppressive regimen after renal transplantation (RTx). However, its metabolism rate is highly variable. A fast Tac metabolism rate, defined by the Tac blood trough concentration (C) divided by the daily dose (D), is associated with inferior renal function after RTx. Therefore, we hypothesize that the Tac metabolism rate impacts patient and graft survival after RTx. We analyzed all patients who received a RTx between January 2007 and December 2012 and were initially treated with an immunosuppressive regimen containing Tac (Prograf®), mycophenolate mofetil, prednisolone and induction therapy. Patients with a Tac C/D ratio <1.05 ng/mL × 1/mg at three months after RTx were characterized as fast metabolizers and those with a C/D ratio ≥1.05 ng/mL×1/mg as slow metabolizers. Five-year patient and overall graft survival were noticeably reduced in fast metabolizers. Further, fast metabolizers showed a faster decline of eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate) within five years after RTx and a higher rejection rate compared to slow metabolizers. Calculation of the Tac C/D ratio three months after RTx may assist physicians in their daily clinical routine to identify Tac-treated patients at risk for the development of inferior graft function, acute rejections, or even higher mortality.
Keywords: C/D-ratio; kidney transplantation; pharmacokinetics; tacrolimus.
Conflict of interest statement
SR received travel support from Astellas, Chiesi, and Pfizer and lecture fees from Chiesi.
Figures

References
-
- Chen S.-Y., Li J.-L., Meng F.-H., Wang X.-D., Liu T., Li J., Liu L.-S., Fu Q., Huang M., Wang C.-X. Individualization of tacrolimus dosage basing on cytochrome P450 3A5 polymorphism—a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Clin. Transplant. 2013;27:E272–E281. doi: 10.1111/ctr.12101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boughton O., Borgulya G., Cecconi M., Fredericks S., Moreton-Clack M., MacPhee I.A.M. A published pharmacogenetic algorithm was poorly predictive of tacrolimus clearance in an independent cohort of renal transplant recipients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013;76:425–431. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

