Application of Acyzol in the Context of Zinc Deficiency and Perspectives
- PMID: 31035445
- PMCID: PMC6539662
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20092104
Application of Acyzol in the Context of Zinc Deficiency and Perspectives
Abstract
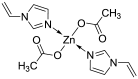
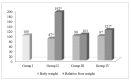
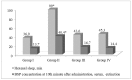
Zinc is one of the most important essential trace elements. It is involved in more than 300 enzyme systems and is an indispensable participant in many biochemical processes. Zinc deficiency causes a number of disorders in the human body, the main ones being the delay of growth and puberty, immune disorders, and cognitive dysfunctions. There are over two billion people in the world suffering from zinc deficiency conditions. Acyzol, a zinc-containing medicine, developed as an antidote against carbon monoxide poisoning, demonstrates a wide range of pharmacological activities: Anti-inflammatory, reparative, detoxifying, immunomodulatory, bacteriostatic, hepatoprotective, adaptogenic, antioxidant, antihypoxic, and cardioprotective. The presence of zinc in the composition of Acyzol suggests the potential of the drug in the treatment and prevention of zinc deficiency conditions, such as Prasad's disease, immune system pathology, alopecia, allergodermatoses, prostate dysfunction, psoriasis, stomatitis, periodontitis, and delayed mental and physical development in children. Currently, the efficiency of Acyzol in the cases of zinc deficiency is shown in a large number of experimental studies. So, Acyzol can be used as a highly effective drug for pharmacologic therapy of a wide range of diseases and conditions and it opens up new perspectives in the treatment and prevention of zinc deficiency conditions.
Keywords: Acyzol; carbon monoxide; pharmacological activity; zinc; zinc deficiency conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Torshin I.Y. Bioinformatics in the Post-Genomic Era: Sensing the Change from Molecular Genetics to Personalized Medicine. Nova Biomedical Books; New York, NY, USA: 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

