An Update on Interleukin-9: From Its Cellular Source and Signal Transduction to Its Role in Immunopathogenesis
- PMID: 31035677
- PMCID: PMC6522352
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20092113
An Update on Interleukin-9: From Its Cellular Source and Signal Transduction to Its Role in Immunopathogenesis
Abstract
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) is a pleiotropic cytokine and was primarily studied in the context of T helper 2 (TH2)-associated immuno-pathological conditions such as asthma and parasitic infections. There was a paradigm shift in the biology of IL-9 after the recent discovery of TH9 cells, a new subtype of TH cells which secrete IL-9 in copious amounts. This has resulted in renewed interest in this cytokine, which was neglected since discovery because it was considered it to be just another TH2 cytokine. Recent studies have shown that it has multiple cellular sources and is critically involved in the immune-pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases and in guarding immune tolerance. In this review, we will discuss its discovery, gene organization, cellular sources, and signaling pathways. Especially, we will give an update on the recent development regarding its relevance in the immune pathogenesis of human diseases.
Keywords: inflammatory diseases; interleukin-9; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
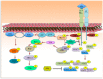

References
-
- Hultner L., Moeller J., Schmitt E., Jäger G., Reisbach G., Ring J., Dörmer P. Thiol-sensitive mast cell lines derived from mouse bone marrow respond to a mast cell growth-enhancing activity different from both IL-3 and IL-4. J. Immunol. 1989;142:3440–3446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

