Berberine in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics
- PMID: 31037148
- PMCID: PMC6485276
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.30787
Berberine in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics
Abstract
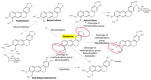
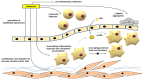
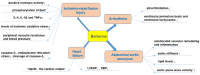
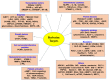
Cardiovascular and metabolic diseases (CVMD) are the leading causes of death worldwide, underscoring the urgent necessity to develop new pharmacotherapies. Berberine (BBR) is an eminent component of traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for more than 2000 years. Recently, BBR has attracted much interest for its pharmacological actions in treating and/or managing CVMD. Recent discoveries of basic, translational and clinical studies have identified many novel molecular targets of BBR (such as AMPK, SIRT1, LDLR, PCSK9, and PTP1B) and provided novel evidences supporting the promising therapeutic potential of BBR to combat CVMD. Thus, this review provides a timely overview of the pharmacological properties and therapeutic application of BBR in CVMD, and underlines recent pharmacological advances which validate BBR as a promising lead drug against CVMD.
Keywords: berberine; cardiovascular diseases; metabolic diseases; targets; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Chandirasegaran G, Elanchezhiyan C, Ghosh K. Effects of Berberine chloride on the liver of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in albino Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:227–36. - PubMed
-
- Xu S, Bai P, Little PJ, Liu P. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) in atherosclerosis: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2014;34:644–75. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S. et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e67–e492. - PubMed
-
- Timmis A, Townsend N, Gale C, Grobbee R, Maniadakis N, Flather M. et al. European Society of Cardiology: Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:508–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

