A novel human IL2RB mutation results in T and NK cell-driven immune dysregulation
- PMID: 31040184
- PMCID: PMC6547857
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20182015
A novel human IL2RB mutation results in T and NK cell-driven immune dysregulation
Erratum in
-
Correction: A novel human IL2RB mutation results in T and NK cell-driven immune dysregulation.J Exp Med. 2019 Jun 3;216(6):1465. doi: 10.1084/jem.2018201505102019c. Epub 2019 May 14. J Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31088899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The pleiotropic actions of interleukin-2 (IL-2) are essential for regulation of immune responses and maintenance of immune tolerance. The IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) is composed of IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ subunits, with defects in IL-2Rα and IL-2Rγ and their downstream signaling effectors resulting in known primary immunodeficiency disorders. Here, we report the first human defect in IL-2Rβ, occurring in two infant siblings with a homozygous IL2RB mutation in the WSXWS motif, manifesting as multisystem autoimmunity and susceptibility to CMV infection. The hypomorphic mutation results in diminished IL-2Rβ surface expression and dysregulated IL-2/15 signaling, with an anticipated reduction in regulatory T cells. However, in contrast to the IL-2Rβ-/- animal model, which lacks NK cells, these siblings demonstrate an expansion of NK cells, particularly the CD56bright subset, and a lack of terminally differentiated NK cells. Thus, the early-onset autoimmunity and immunodeficiency are linked to functional deficits arising from altered IL-2Rβ expression and signaling in T and NK cells.
© 2019 Fernandez et al.
Figures
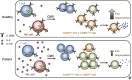
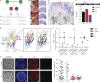
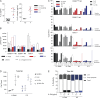
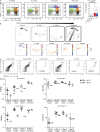

Comment in
-
IL2RB maintains immune harmony.J Exp Med. 2019 Jun 3;216(6):1231-1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190546. Epub 2019 May 8. J Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31068380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amir A.D., Davis K.L., Tadmor M.D., Simonds E.F., Levine J.H., Bendall S.C., Shenfeld D.K., Krishnaswamy S., Nolan G.P., and Pe’er D.. 2013. viSNE enables visualization of high dimensional single-cell data and reveals phenotypic heterogeneity of leukemia. Nat. Biotechnol. 31:545–552. 10.1038/nbt.2594 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner J.W., Wells C.A., Chen C.M., and Waters M.J.. 1994. The role of the WSXWS equivalent motif in growth hormone receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 269:29094–29101. - PubMed
-
- Bennett C.L., Christie J., Ramsdell F., Brunkow M.E., Ferguson P.J., Whitesell L., Kelly T.E., Saulsbury F.T., Chance P.F., and Ochs H.D.. 2001. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat. Genet. 27:20–21. 10.1038/83713 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi A., Marino R., Ribas A., Rossi J., Ciaccio M., Oleastro M., Ornani A., Paz R., Rivarola M.A., Zelazko M., and Belgorosky A.. 2006. Characterization of immunodeficiency in a patient with growth hormone insensitivity secondary to a novel STAT5b gene mutation. Pediatrics. 118:e1584–e1592. 10.1542/peds.2005-2882 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI126899/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007405/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101205/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008497/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI131302/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK100461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR070897/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM123169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL068702/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001084/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI066121/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA102667/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

