Liver-target nanotechnology facilitates berberine to ameliorate cardio-metabolic diseases
- PMID: 31040273
- PMCID: PMC6491597
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09852-0
Liver-target nanotechnology facilitates berberine to ameliorate cardio-metabolic diseases
Abstract
Cardiovascular and metabolic disease (CMD) remains a main cause of premature death worldwide. Berberine (BBR), a lipid-lowering botanic compound with diversified potency against metabolic disorders, is a promising candidate for ameliorating CMD. The liver is the target of BBR so that liver-site accumulation could be important for fulfilling its therapeutic effect. In this study a rational designed micelle (CTA-Mic) consisting of α-tocopheryl hydrophobic core and on-site detachable polyethylene glycol-thiol shell is developed for effective liver deposition of BBR. The bio-distribution analysis proves that the accumulation of BBR in liver is increased by 248.8% assisted by micelles. Up-regulation of a range of energy-related genes is detectable in the HepG2 cells and in vivo. In the high fat diet-fed mice, BBR-CTA-Mic intervention remarkably improves metabolic profiles and reduces the formation of aortic arch plaque. Our results provide proof-of-concept for a liver-targeting strategy to ameliorate CMD using natural medicines facilitated by Nano-technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

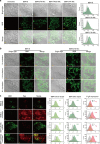
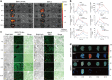

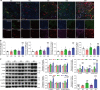

References
-
- Catapano AL, et al. 2016 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: The Task Force for the Management of Dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Developed with the special contribution of the European Assocciation for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR) Atherosclerosis. 2016;253:281–344. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.08.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

