Nutritional status of the student nurses of a tertiary health-care center - A mixed-method study
- PMID: 31041246
- PMCID: PMC6482778
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_314_18
Nutritional status of the student nurses of a tertiary health-care center - A mixed-method study
Abstract
Context: Nursing students are the future role model of health; so critical evaluation of their nutritional status is imperative for effective functioning of health sector.
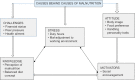
Aims: The aim is to assess the nutritional status of nursing students using basal metabolic index and exploring the causes of malnutrition along with uncovering the causes behind these causes of malnutrition.
Setting and design: Nutritional status of student's nurses was assessed by mixed-method study design in tertiary care center of Mumbai, India.
Materials and methods: The method is to use the census method for sampling 280 nursing students of a tertiary care center interviewed using a semistructured interview schedule. Focus group discussions were held with student nurses, which were selected through purposive sampling technique to interpret the instigator causes behind causes of malnutrition.
Statistical analysis: Descriptive statistics was applied on qualitative data. Conceptual model framed on themes and subthemes based upon the codes from qualitative data.
Results: Students having BMI less than 18 and more than 24.9 were 189 and 11, respectively, out of 280 students. About 64.20% had acidity and 11.07% performed regular exercises evolving major themes: challenges, stress, attitude, knowledge, social barriers, and motivators.
Conclusion: About 67.5% of nursing students had BMI less than 18. Inappropriate dietary pattern, frequent ailments, and improper personal habits ensued their malnourished status. Lack of proper knowledge on balanced diet, work place stress, and challenges such as financial constrain, peer pressure, and health ailments along with improper perception of body image of the student nurses are major triggering factors behind the causes of malnutrition.
Keywords: Diet; malnutrition causes; student nurses.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shortage N, Margo Brooks Carthon J, Nguyen TH, Pancir D, Chittams J, Burnett L, et al. Council for nursing released a joint statement on recent registered nurse supply and demand projections. Nurse Educ Today. 2013;65:1–6.
-
- Bhaumik S. Workforce planning. Why is India short of nurses and what can we do about it? BMJ. 2013:346. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f4024. - PubMed
-
- Needleman J, Buerhaus P, Pankratz VS, Leibson CL, Stevens SR, Harris M. Nurse staffing and inpatient hospital mortality. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1037–45. - PubMed