Is Burnout Infectious? Understanding Drivers of Burnout and Job Satisfaction Among Academic Infectious Diseases Physicians
- PMID: 31041336
- PMCID: PMC6483804
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofz092
Is Burnout Infectious? Understanding Drivers of Burnout and Job Satisfaction Among Academic Infectious Diseases Physicians
Abstract
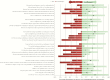
Burnout is pervasive in academic medicine. We administered the Maslach Burnout Inventory and an Infectious Diseases (ID) job description survey to our ID faculty. Respondents' burnout (>50%) and job satisfaction (>90%) were each high. Although burnout may be balanced by job satisfaction, the relationship between the 2 deserves further study.
Keywords: burnout; infectious diseases specialists; job description; job satisfaction.
Figures
References
-
- Lagnado L. Hospitals adress widespread doctor burnout. The Wall Street Journal. 2018. Available at: https://www.wsj.com/articles/hospitals-address-widespread-doctor-burnout.... Accessed 29 June 2018.
-
- Mayo Clinic. Job burnout: How to spot it and take action. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/burno.... Accessed 29 June 2018.
-
- Swensen S, Shanafelt T, Mohta N. Leadership Survey: why physician burnout is endemic, and how health care must respond. NEJM Catalyst 2016. Available at https://catalyst.nejm.org/physician-burnout-endemic-healthcare-respond/. Accessed 29 June 2018.
-
- Eisenstein L. To fight burnout, organize. N Engl J Med 2018; 379:509–11. - PubMed
-
- Wright AA, Katz IT. Beyond burnout - Redesigning care to restore meaning and sanity for physicians. N Engl J Med 2018; 378:309–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases