May Measurement Month 2018: a pragmatic global screening campaign to raise awareness of blood pressure by the International Society of Hypertension
- PMID: 31041440
- PMCID: PMC6600128
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz300
May Measurement Month 2018: a pragmatic global screening campaign to raise awareness of blood pressure by the International Society of Hypertension
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: May Measurement Month 2018: a pragmatic global screening campaign to raise awareness of blood pressure by the International Society of Hypertension.Eur Heart J. 2019 Oct 1;40(37):3109. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz373. Eur Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31132104 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: Raised blood pressure (BP) is the biggest contributor to mortality and disease burden worldwide and fewer than half of those with hypertension are aware of it. May Measurement Month (MMM) is a global campaign set up in 2017, to raise awareness of high BP and as a pragmatic solution to a lack of formal screening worldwide. The 2018 campaign was expanded, aiming to include more participants and countries.
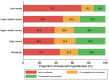
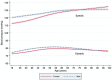
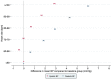
Methods and results: Eighty-nine countries participated in MMM 2018. Volunteers (≥18 years) were recruited through opportunistic sampling at a variety of screening sites. Each participant had three BP measurements and completed a questionnaire on demographic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Hypertension was defined as a systolic BP ≥140 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥90 mmHg, or taking antihypertensive medication. In total, 74.9% of screenees provided three BP readings. Multiple imputation using chained equations was used to impute missing readings. 1 504 963 individuals (mean age 45.3 years; 52.4% female) were screened. After multiple imputation, 502 079 (33.4%) individuals had hypertension, of whom 59.5% were aware of their diagnosis and 55.3% were taking antihypertensive medication. Of those on medication, 60.0% were controlled and of all hypertensives, 33.2% were controlled. We detected 224 285 individuals with untreated hypertension and 111 214 individuals with inadequately treated (systolic BP ≥ 140 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥ 90 mmHg) hypertension.
Conclusion: May Measurement Month expanded significantly compared with 2017, including more participants in more countries. The campaign identified over 335 000 adults with untreated or inadequately treated hypertension. In the absence of systematic screening programmes, MMM was effective at raising awareness at least among these individuals at risk.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Control; Global; Hypertension; Screening; Treatment.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Believing impossible things: achieving universal blood pressure awareness on a global basis.Eur Heart J. 2019 Jul 1;40(25):2018-2020. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz413. Eur Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31209462 No abstract available.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018;392:1923–1994. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whlton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whlton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005;265:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Gupta R, Avezum A, Bahonar A, Chifamba J, Dagenais G, Diaz R, Kazmi K, Lanas F, Wei L, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Fanghong L, Ismail NH, Puoane T, Rosengren A, Szuba A, Temizhan A, Wielgosz A, Yusuf A, Yusufali A, McKee M, Liu L, Mony P, Yusuf S; PURE (Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology) Study investigators. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA 2013;310:959–968. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Lu Y, Wang X, Li X, Linderman GC, Wu C, Cheng X, Mu L, Zhang H, Liu J, Su M, Zhao H, Spatz ES, Spertus JA, Masoudi FA, Krumholz HM, Jiang L.. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China: data from 1.7 million adults in a population-based screening study (China PEACE Million Persons Project). Lancet 2017;390: 2549–2558. - PubMed

