GC/MS-based metabolomics strategy to analyze the effect of exercise intervention in diabetic rats
- PMID: 31042671
- PMCID: PMC6528492
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-19-0012
GC/MS-based metabolomics strategy to analyze the effect of exercise intervention in diabetic rats
Abstract
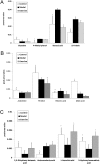
Metabolomics was used to explore the effect of exercise intervention on type 2 diabetes. The rat model of type 2 diabetes was induced by an injection of streptozocin (30 mg/kg), after fed with 8-week high-fat diet. The rats were divided into three groups: the control group, the diabetic model group (DM) and the diabetes + exercise group (DME). After exercise for 10 weeks, blood samples were collected to test biomedical indexes, and 24-h urine samples were collected for the metabolomics experiment. In the DME group, fasting blood glucose (FBG), both total cholesterol (TC) and total plasma triglycerides (TG), were decreased significantly, compared with those in the DM group. Based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS), a urinary metabolomics method was used to study the mechanism of exercise intervention on diabetes mellitus. Based on the principal component analysis (PCA), it was found that the DM group and control group were separated into two different clusters. The DME group was located between the DM group and the control group, closer to the control group. Twelve significantly changed metabolites of diabetes mellitus were detected and identified, including glycolate, 4-methyl phenol, benzoic acid, 1H-indole, arabinitol, threitol, ribonic acid, malic acid, 2,3-dihydroxy-butanoic, aminomalonic acid, l-ascorbic acid and 3-hydroxy hexanedioic acid. After exercise, seven metabolites were significantly changed, compared with the control group, the relative contents of benzoic acid, aminomalonic acid, tetrabutyl alcohol and ribonucleic acid in the diabetic exercise group decreased significantly. The relative contents of 2,3-dihydroxybutyric acid, l-ascorbic acid and 3-hydroxy adipic acid increased significantly. l-ascorbic acid and aminomalonic acid which related with the oxidative stress were significantly regulated to normal. The results showed that exercise could display anti-hyperglycemic and anti-hyperlipidemic effects. The exercise had antioxidation function in preventing the occurrence of complications with diabetes mellitus to some extent. The work illustrates that the metabolomics method is a useful tool to study the mechanism of exercise treatment.
Keywords: exercise; gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; metabolomics; type 2 diabetes.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

