CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 31043744
- PMCID: PMC6533917
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1170-y
CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
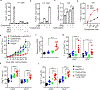
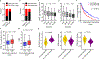
Cancer immunotherapy restores or enhances the effector function of CD8+ T cells in the tumour microenvironment1,2. CD8+ T cells activated by cancer immunotherapy clear tumours mainly by inducing cell death through perforin-granzyme and Fas-Fas ligand pathways3,4. Ferroptosis is a form of cell death that differs from apoptosis and results from iron-dependent accumulation of lipid peroxide5,6. Although it has been investigated in vitro7,8, there is emerging evidence that ferroptosis might be implicated in a variety of pathological scenarios9,10. It is unclear whether, and how, ferroptosis is involved in T cell immunity and cancer immunotherapy. Here we show that immunotherapy-activated CD8+ T cells enhance ferroptosis-specific lipid peroxidation in tumour cells, and that increased ferroptosis contributes to the anti-tumour efficacy of immunotherapy. Mechanistically, interferon gamma (IFNγ) released from CD8+ T cells downregulates the expression of SLC3A2 and SLC7A11, two subunits of the glutamate-cystine antiporter system xc-, impairs the uptake of cystine by tumour cells, and as a consequence, promotes tumour cell lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. In mouse models, depletion of cystine or cysteine by cyst(e)inase (an engineered enzyme that degrades both cystine and cysteine) in combination with checkpoint blockade synergistically enhanced T cell-mediated anti-tumour immunity and induced ferroptosis in tumour cells. Expression of system xc- was negatively associated, in cancer patients, with CD8+ T cell signature, IFNγ expression, and patient outcome. Analyses of human transcriptomes before and during nivolumab therapy revealed that clinical benefits correlate with reduced expression of SLC3A2 and increased IFNγ and CD8. Thus, T cell-promoted tumour ferroptosis is an anti-tumour mechanism, and targeting this pathway in combination with checkpoint blockade is a potential therapeutic approach.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

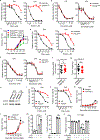



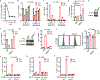

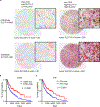
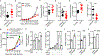

Comment in
-
Immunotherapy Activates Unexpected Cell Death Mechanism.Cancer Discov. 2019 Jul;9(7):OF2. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2019-058. Epub 2019 May 21. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 31113802
-
Interferon-γ induces cancer cell ferroptosis.Cell Res. 2019 Sep;29(9):692-693. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0186-z. Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31160718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Physiological Function for Ferroptosis in Tumor Suppression by the Immune System.Cell Metab. 2019 Jul 2;30(1):14-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.012. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 31269423 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA189623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA189623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA152470/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA211016/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA099985/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA193136/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA217510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA205426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA214911/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127648/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA232097/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

