Establishing funding rates for colonoscopy and gastroscopy procedures in Ontario
- PMID: 31043810
- PMCID: PMC6476446
- DOI: 10.3747/co.26.4405
Establishing funding rates for colonoscopy and gastroscopy procedures in Ontario
Abstract
Introduction: This paper describes the funding rates established in Ontario to reflect best practices in hospital-based care delivery for these endoscopic procedures: colonoscopy, colonoscopy biopsy, gastroscopy, gastroscopy biopsy, and colonoscopy combined with gastroscopy.
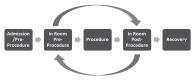
Methods: The funding rates are based on direct costs and were established using a micro-costing approach after receipt of inputs from 3 working groups and a review of the administrative data and literature, where applicable. The first group advised on nursing activities, time, and staffing ratios along the patient pathway for each of the procedures. The second group provided recommendations about the duration for each procedure, and the third group provided information about supplies and equipment, their use, and costs.
Results: The resulting funding rates are $161.18 for colonoscopy and $151.08 for gastroscopy (without accompanying interventions), $16.06 for colonoscopy biopsy and $8.22 for gastroscopy biopsy (added to the respective procedures), and $207.26 for combined colonoscopy and gastroscopy. Detailed costs for each component embedded in the rates are also provided.
Conclusions: The rates came into effect in April 2018. The process and outcomes described here allowed for a transparent pricing mechanism in which funding follows the patient, clinical expert consensus is the basis for practice, and providers and payers both understand the components.
Keywords: Colonoscopy costs; funding rates; gastroscopy costs; micro-costing.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES We have read and understood Current Oncology’s policy on disclosing conflicts of interest, and we declare that we have none.
References
-
- Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. Health System Funding Reform (HSFR) [Web page] Toronto, ON: Queen’s Printer for Ontario; 2015. [Available at: http://www.health.gov.on.ca/en/pro/programs/ecfa/funding/hs_funding.aspx; cited 6 August 2018]
-
- Canadian Institute for Health Information (cihi) Discharge Abstract Database. Ottawa, ON: cihi; n.d..
-
- Canadian Institute for Health Information (cihi) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System database. Ottawa, ON: cihi; n.d..
-
- Ontario, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (mohltc) Health System Funding Reform: quality-based procedures [Web page] Toronto, ON: Queen’s Printer for Ontario; 2018. [Available at: http://www.health.gov.on.ca/en/pro/programs/ecfa/funding/hs_funding_qbp....; cited 6 August 2018]
-
- Ontario, Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care (mohltc) Quality-Based Procedures Clinical Handbook for GI Endoscopy. Toronto, ON: mohltc; 2015. [Available online at: http://www.health.gov.on.ca/en/pro/programs/ecfa/docs/qbp_gi.pdf; cited 6 August 2018]
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous